Adolescent Balloon Analog Risk Task and Behaviors that Influence Risk of Motor Vehicle Crash Injury
- PMID: 24406948
- PMCID: PMC3861840
Adolescent Balloon Analog Risk Task and Behaviors that Influence Risk of Motor Vehicle Crash Injury
Abstract
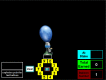
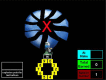
Risk-taking propensity is a pivotal facet of motor vehicle crash involvement and subsequent traumatic injury in adolescents. Clinical encounters are important opportunities to identify teens with high risk-taking propensity who may later experience serious injury. Our objective was to compare self-reports of health risk behavior with performance on the Balloon Analog Risk Task (BART), a validated metric of risk-taking propensity, in adolescents during a clinical encounter. 100 adolescent patients from a hospital emergency department and adolescent health clinic completed a computer-based survey of self-reported risk behaviors including substance use behaviors and behaviors that influence crash involvement. They then completed the BART, a validated laboratory-based risk task in which participants earn points by pumping up a computer-generated balloon with greater pumps leading to increased chance of balloon explosion. 20 trials were undertaken. Mean number of pumps on the BART showed a correlation of .243 (p=.015) with self-reported driver/passenger behaviors and attitudes towards driving that influence risk of crash injury. Regression analyses showed that self-reports of substance use and mean number of pumps on the BART uniquely predict self-reports of behaviors influencing the risk of crash injury. The BART is a promising correlate of real-world risk-taking behavior related to traffic safety. It remains a valid predictor of behaviors influencing risk of crash injury when using just 10 trials, suggesting its utility as a quick and effective screening measure for use in busy clinical environments. This tool may be an important link to prevention interventions for those most at-risk for future motor vehicle crash involvement and injury.
Figures
References
-
- Aklin WM, Lejuez CW, Zvolensky MJ, Kahler CW, Gwadz M. Evaluation of behavioral measures of risk taking propensity with inner city adolescents. Behav Res Ther. 2005;43(2):215–28. - PubMed
-
- Arnett J. Reckless behavior in adolescence: A developmental perspective. Dev Rev. 1992;12(4):339–373.
-
- Bernstein DM, Whittlesea BW, Loftus EF. Increasing confidence in remote autobiographical memory and general knowledge: extensions of the revelation effect. Mem Cognit. 2002;30(3):432–8. - PubMed
-
- Bina M, Graziano F, Bonino S. Risky driving and lifestyles in adolescence. Accid Anal Prev. 2006;38(3):472–481. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources