Human copper-dependent amine oxidases
- PMID: 24407025
- PMCID: PMC5995473
- DOI: 10.1016/j.abb.2013.12.022
Human copper-dependent amine oxidases
Abstract
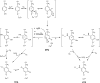
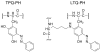
Copper amine oxidases (CAOs) are a class of enzymes that contain Cu(2+) and a tyrosine-derived quinone cofactor, catalyze the conversion of a primary amine functional group to an aldehyde, and generate hydrogen peroxide and ammonia as byproducts. These enzymes can be classified into two non-homologous families: 2,4,5-trihydroxyphenylalanine quinone (TPQ)-dependent CAOs and the lysine tyrosylquinone (LTQ)-dependent lysyl oxidase (LOX) family of proteins. In this review, we will focus on recent developments in the field of research concerning human CAOs and the LOX family of proteins. The aberrant expression of these enzymes is linked to inflammation, fibrosis, tumor metastasis/invasion and other diseases. Consequently, there is a critical need to understand the functions of these proteins at the molecular level, so that strategies targeting these enzymes can be developed to combat human diseases.
Keywords: Copper amine oxidase; Lysyl oxidase; Quinoprotein.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

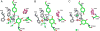
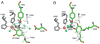


References
-
- Klinman JP. New quinocofactors in eukaryotes. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:27189–27192. - PubMed
-
- Csiszar K. Lysyl oxidases: a novel multifunctional amine oxidase family. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 2001;70:1–32. - PubMed
-
- Dubois JL, Klinman JP. Mechanism of post-translational quinone formation in copper amine oxidases and its relationship to the catalytic turnover. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2005;433:255–265. - PubMed
-
- Jalkanen S, Salmi M. Vascular adhesion protein-1 (VAP-1)--a new adhesion molecule recruiting lymphocytes to sites of inflammation. Res Immunol. 1993;144:746–749. discussion 754-762. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

