Kruppel-like factor 15 is a critical regulator of cardiac lipid metabolism
- PMID: 24407292
- PMCID: PMC3937660
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.531384
Kruppel-like factor 15 is a critical regulator of cardiac lipid metabolism
Abstract
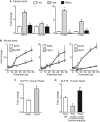
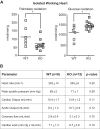
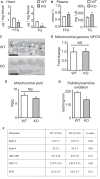
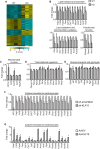
The mammalian heart, the body's largest energy consumer, has evolved robust mechanisms to tightly couple fuel supply with energy demand across a wide range of physiologic and pathophysiologic states, yet, when compared with other organs, relatively little is known about the molecular machinery that directly governs metabolic plasticity in the heart. Although previous studies have defined Kruppel-like factor 15 (KLF15) as a transcriptional repressor of pathologic cardiac hypertrophy, a direct role for the KLF family in cardiac metabolism has not been previously established. We show in human heart samples that KLF15 is induced after birth and reduced in heart failure, a myocardial expression pattern that parallels reliance on lipid oxidation. Isolated working heart studies and unbiased transcriptomic profiling in Klf15-deficient hearts demonstrate that KLF15 is an essential regulator of lipid flux and metabolic homeostasis in the adult myocardium. An important mechanism by which KLF15 regulates its direct transcriptional targets is via interaction with p300 and recruitment of this critical co-activator to promoters. This study establishes KLF15 as a key regulator of myocardial lipid utilization and is the first to implicate the KLF transcription factor family in cardiac metabolism.
Keywords: Cardiac Metabolism; Cardiovascular; Kruppel-like Factor (KLF); Lipid Metabolism; Transcription Factors.
Figures


References
-
- Lopaschuk G. D., Ussher J. R., Folmes C. D., Jaswal J. S., Stanley W. C. (2010) Myocardial fatty acid metabolism in health and disease. Physiol. Rev. 90, 207–258 - PubMed
-
- Bertrand L., Horman S., Beauloye C., Vanoverschelde J. L. (2008) Insulin signalling in the heart. Cardiovasc. Res. 79, 238–248 - PubMed
-
- Neubauer S. (2007) The failing heart. An engine out of fuel. N. Engl. J. Med. 356, 1140–1151 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- HL074237/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL105338/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- HL086614/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- CA132977/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K23 HL095742/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL072952/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 HD068546/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- P30 HL101272/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- F32 HL110538/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 HL086614/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL095742/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL119195/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1RR024143/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- F32HL110538/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL101272/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA043703/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL084154/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL112486/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL074237/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL072952/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- CA043703/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- DK093821/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024143/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA132977/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32HL105338/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL084154/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK093821/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

