Noninvasive micromarkers
- PMID: 24407912
- PMCID: PMC4149835
- DOI: 10.1373/clinchem.2013.216044
Noninvasive micromarkers
Abstract
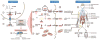
Background: The recent revolutionary advances made in genome-wide sequencing technology have transformed biology and molecular diagnostics, allowing new sRNA (small RNA) classes to be discovered as potential disease-specific biological indicators. Cell-free microRNAs (miRNAs) have been shown to exist stably in a wide spectrum of body fluids and their expression profiles have been shown to reflect an assortment of physiological conditions, underscoring the utility of this new class of molecules to function as noninvasive biomarkers of disease.
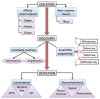
Content: We summarize information on the known mechanisms of miRNA protection and release into extracellular space and compile the current literature on extracellular miRNAs that have been investigated as biomarkers of 20 different cancers, 11 organ damage conditions and 10 diverse disease states. We also discuss the various strategies involved in the miRNA biomarker discovery workflow and provide a critical opinion on the impediments faced by this advancing field that need to be overcome in the laboratory.
Summary: The field of miRNA-centered diagnostics is still in its infancy, and basic questions with regard to the exact role of miRNAs in the pathophysiology of diseases, and the mechanisms of their release from affected cells into biological fluids are yet to be completely understood. Nevertheless, these noninvasive micromarkers have immense potential in translational medicine not only for use in monitoring the efficacy and safety of therapeutic regimens but also to guide the diagnosis of diseases, to determine the risk of developing diseases or conditions, and more importantly, to inform treatment options.
© 2013 American Association for Clinical Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Lee R, Feinbaum R, Ambros V. The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell. 1993;75:843–54. - PubMed
-
- Reinhart B, Slack F, Basson M, Pasquinelli A, Bettinger J, Rougvie A, et al. The 21-nucleotide let-7 RNA regulates developmental timing in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 2000;403:901–6. - PubMed
-
- Pasquinelli A, Reinhart B, Slack F, Martindale M, Kuroda M, Maller B, et al. Conservation of the sequence and temporal expression of let-7 heterochronic regulatory RNA. Nature. 2000;408:86–9. - PubMed
-
- Winter J, Jung S, Keller S, Gregory RI, Diederichs S. Many roads to maturity: microRNA biogenesis pathways and their regulation. Nat Cell Biol. 2009;11:228–34. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

