Activation of IL-27 signalling promotes development of postinfluenza pneumococcal pneumonia
- PMID: 24408967
- PMCID: PMC3936494
- DOI: 10.1002/emmm.201302890
Activation of IL-27 signalling promotes development of postinfluenza pneumococcal pneumonia
Abstract
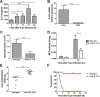
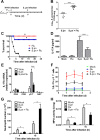
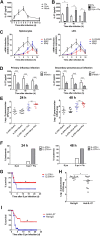
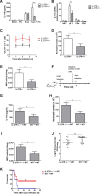
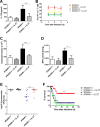
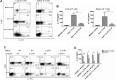
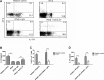
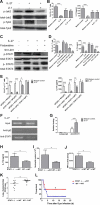
Postinfluenza pneumococcal pneumonia is a common cause of death in humans. However, the role of IL-27 in the pathogenesis of secondary pneumococcal pneumonia after influenza is unknown. We now report that influenza infection induced pulmonary IL-27 production in a type I IFN-α/β receptor (IFNAR) signalling-dependent manner, which sensitized mice to secondary pneumococcal infection downstream of IFNAR pathway. Mice deficient in IL-27 receptor were resistant to secondary pneumococcal infection and generated more IL-17A-producing γδ T cells but not αβ T cells, thereby leading to enhanced neutrophil response during the early phase of host defence. IL-27 treatment could suppress the development of IL-17A-producing γδ T cells activated by Streptococcus pneumoniae and dendritic cells. This suppressive activity of IL-27 on γδ T cells was dependent on transcription factor STAT1. Finally, neutralization of IL-27 or administration of IL-17A restored the role of γδ T cells in combating secondary pneumococcal infection. Our study defines what we believe to be a novel role of IL-27 in impairing host innate immunity against pneumococcal infection.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Interleukin-35 is upregulated in response to influenza virus infection and secondary bacterial pneumonia.Cytokine. 2016 May;81:23-7. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2016.01.016. Epub 2016 Feb 5. Cytokine. 2016. PMID: 26844658
-
IL-10 is an important mediator of the enhanced susceptibility to pneumococcal pneumonia after influenza infection.J Immunol. 2004 Jun 15;172(12):7603-9. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.172.12.7603. J Immunol. 2004. PMID: 15187140
-
Limited anti-inflammatory role for interleukin-1 receptor like 1 (ST2) in the host response to murine postinfluenza pneumococcal pneumonia.PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e58191. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0058191. Epub 2013 Mar 6. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23483993 Free PMC article.
-
Type I interferon induction during influenza virus infection increases susceptibility to secondary Streptococcus pneumoniae infection by negative regulation of γδ T cells.J Virol. 2012 Nov;86(22):12304-12. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01269-12. Epub 2012 Sep 5. J Virol. 2012. PMID: 22951826 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of the platelet-activating factor receptor in host defense against Streptococcus pneumoniae during postinfluenza pneumonia.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2006 Jan;290(1):L194-9. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00050.2005. Epub 2005 Aug 12. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16100290
Cited by
-
The past, present and future of RNA respiratory viruses: influenza and coronaviruses.Pathog Dis. 2020 Oct 7;78(7):ftaa046. doi: 10.1093/femspd/ftaa046. Pathog Dis. 2020. PMID: 32860686 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of γδ T cells in controlling viral infections with a focus on influenza virus: implications for designing novel therapeutic approaches.Virol J. 2020 Nov 12;17(1):174. doi: 10.1186/s12985-020-01449-0. Virol J. 2020. PMID: 33183352 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of Type I Interferons on Susceptibility to Bacterial Pathogens.Trends Microbiol. 2021 Sep;29(9):823-835. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2021.01.007. Epub 2021 Feb 2. Trends Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33546974 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exogenous Activation of Invariant Natural Killer T Cells by α-Galactosylceramide Reduces Pneumococcal Outgrowth and Dissemination Postinfluenza.mBio. 2016 Nov 1;7(6):e01440-16. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01440-16. mBio. 2016. PMID: 27803187 Free PMC article.
-
The host transcriptional response to superinfection by influenza A virus and Streptococcus pneumoniae.mSystems. 2024 Apr 16;9(4):e0104823. doi: 10.1128/msystems.01048-23. Epub 2024 Mar 6. mSystems. 2024. PMID: 38446104 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cao J, Gong Y, Dong S, Zhang L, Lai X, Zhang X, Yin Y. Pneumococcal ClpP modulates the maturation and activation of human dendritic cells: implications for pneumococcal infections. J Leukoc Biol. 2013;93:737–749. - PubMed
-
- Cao J, Gong Y, Yin Y. The role played by interleukin-10 in cytokine and chemokine dysregulation during secondary pneumococcal pneumonia after influenza. J Infect Dis. 2009;199:1555–1556. - PubMed
-
- Cao J, Wong CK, Yin Y, Lam CW. Activation of human bronchial epithelial cells by inflammatory cytokines IL-27 and TNF-alpha: implications for immunopathophysiology of airway inflammation. J Cell Physiol. 2010;223:788–797. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

