TWEAK/Fn14 pathway is a novel mediator of retinal neovascularization
- PMID: 24408972
- PMCID: PMC3920863
- DOI: 10.1167/iovs.13-12812
TWEAK/Fn14 pathway is a novel mediator of retinal neovascularization
Abstract
Purpose: Retinal neovascularization (NV) is a major cause of vision loss in ischemia-induced retinopathy. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-like weak inducer of apoptosis (TWEAK) and its receptor, fibroblast growth factor inducible-14 (Fn14), have been implicated in angiogenesis, but their role in retinal diseases is unknown. The goal of this study was to investigate the role of TWEAK/Fn14 pathway in retinal NV.
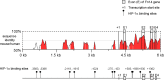
Methods: Studies were performed in a mouse model of oxygen-induced retinopathy (OIR) and in primary human retinal microvascular endothelial cells (HRMECs). Hyperoxia treatment was initiated on postnatal day (P)14. Immunohistochemistry and quantitative PCR (qPCR) were used to assess retinal vascular changes in relation to expression of Fn14 and TWEAK.
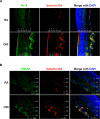
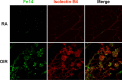
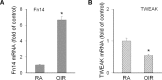
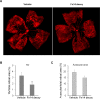
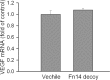
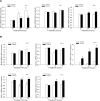
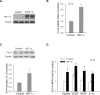
Results: Fibroblast growth factor-inducible 14 mRNA was prominently increased from P13 to P17 in OIR retinas, whereas TWEAK level was slightly decreased. These alterations were normalized by hyperoxia treatment and were more striking in isolated retinal vessels. There was a discernible shift in the immunoreactivity of Fn14 and TWEAK from the neuronal layers in the healthy retina to the neovascular tufts in that of OIR. Blockade of TWEAK/Fn14 significantly prevented retinal NV while slightly accelerated revascularization. In contrast, activation of Fn14 positively regulated survival pathways in the B-cell lymphoma-2 (Bcl2) family and robustly enhanced HRMEC survival. Furthermore, gene analysis revealed the regulatory region of Fn14 gene contains several conserved hypoxia inducible factor (HIF)-1α binding sites. Overexpression of HIF-1α prominently induced Fn14 expression in HRMECs.
Conclusions: We found that the TNF-like weak inducer of apoptosis (TWEAK)/fibroblast growth factor inducible-14 (Fn14) pathway is involved in the development of pathologic retinal neovascularization. Hypoxia inducible factor-1α is likely implicated in the upregulation of Fn14.
Keywords: Fn14; TWEAK; ischemia-induced retinopathy; neovascularization; retina.
Figures
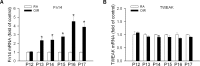


References
-
- Multicenter trial of cryotherapy for retinopathy of prematurity 3 1/2-year outcome–structure and function. Cryotherapy for Retinopathy of Prematurity Cooperative Group. Arch Ophthalmol. 1993; 111: 339–344 - PubMed
-
- Phelps DL. Retinopathy of prematurity. Pediatr Rev. 1995; 16: 50–56 - PubMed
-
- Tsilimbaris MK, Kontadakis GA, Tsika C, Papageorgiou D, Charoniti M. Effect of panretinal photocoagulation treatment on vision-related quality of life of patients with proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Retina. 2013; 33: 756–761 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

