Effectiveness of a hydroxynaphthoquinone fraction from Arnebia euchroma in rats with experimental colitis
- PMID: 24409058
- PMCID: PMC3882404
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i48.9318
Effectiveness of a hydroxynaphthoquinone fraction from Arnebia euchroma in rats with experimental colitis
Abstract
Aim: To evaluate the potential effectiveness of hydroxynaphthoquinone mixture (HM) in rats with 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid (TNBS)-induced colitis.
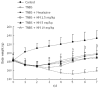
Methods: Colitis was induced by intracolonic administration of TNBS (80 mg/kg, dissolved in 50% ethanol). Rats were treated daily for 7 d with HM (2.5, 5, 10 mg/kg) and mesalazine 100 mg/kg 24 h after TNBS instillation. Disease progression was monitored daily by observation of clinical signs and body weight change. At the end of the experiment, macroscopic and histopathologic lesions of rats were scored, and myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity was determined. We also determined inflammatory cytokine tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α level by ELISA, Western blotting and immunochemistry to explore the potential mechanisms of HM.
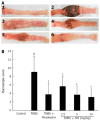
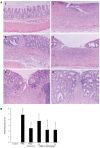
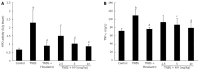
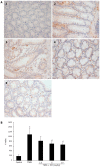
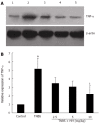
Results: After intracolonic instillation of TNBS, animals developed colitis associated with soft stool, diarrhea and marked colonic destruction. Administration of HM significantly attenuated clinical and histopathologic severity of TNBS-induced colitis in a dose-dependent manner. It abrogated body weight loss, diarrhea and inflammation, decreased macroscopic damage score, and improved histological signs, with a significant reduction of inflammatory infiltration, ulcer size and the severity of goblet cell depletion (all P < 0.05 vs TNBS alone group). HM could reduce MPO activity. In addition, it also decreased serum TNF-α level and down-regulated TNF-α expression in colonic tissue. This reduction was statistically significant when the dose of HM was 10 mg/kg (P < 0.05 vs TNBS alone group), and the effect was comparable to that of mesalazine and showed no apparent adverse effect. The underlying mechanism may be associated with TNF-α inhibition.
Conclusion: These findings suggest that HM possesses favourable therapeutic action in TNBS-induced colitis, which provides direct pharmacological evidence for its clinical application.
Keywords: 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid-induced colitis; Arnebia euchroma (Royle) Johnst; Hydroxynaphthoquinones; Inflammatory bowel disease; Tumor necrosis factor.
Figures
References
-
- Hanauer SB. Inflammatory bowel disease: epidemiology, pathogenesis, and therapeutic opportunities. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2006;12 Suppl 1:S3–S9. - PubMed
-
- Cosnes J, Gower-Rousseau C, Seksik P, Cortot A. Epidemiology and natural history of inflammatory bowel diseases. Gastroenterology. 2011;140:1785–1794. - PubMed
-
- Huang ZS, Zhang M, Ma L, Gu LQ. A survery of chemical and pharmacologic studies on Zicao. Tianranchanwu Yanjiu Yu Kaifa. 1999;12:73–82.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

