Update on the Angiotensin converting enzyme 2-Angiotensin (1-7)-MAS receptor axis: fetal programing, sex differences, and intracellular pathways
- PMID: 24409169
- PMCID: PMC3886117
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2013.00201
Update on the Angiotensin converting enzyme 2-Angiotensin (1-7)-MAS receptor axis: fetal programing, sex differences, and intracellular pathways
Abstract
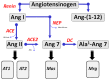
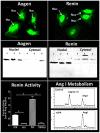
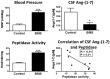
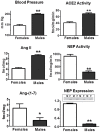
The renin-angiotensin-system (RAS) constitutes an important hormonal system in the physiological regulation of blood pressure. Indeed, dysregulation of the RAS may lead to the development of cardiovascular pathologies including kidney injury. Moreover, the blockade of this system by the inhibition of angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) or antagonism of the angiotensin type 1 receptor (AT1R) constitutes an effective therapeutic regimen. It is now apparent with the identification of multiple components of the RAS that the system is comprised of different angiotensin peptides with diverse biological actions mediated by distinct receptor subtypes. The classic RAS can be defined as the ACE-Ang II-AT1R axis that promotes vasoconstriction, sodium retention, and other mechanisms to maintain blood pressure, as well as increased oxidative stress, fibrosis, cellular growth, and inflammation in pathological conditions. In contrast, the non-classical RAS composed of the ACE2-Ang-(1-7)-Mas receptor axis generally opposes the actions of a stimulated Ang II-AT1R axis through an increase in nitric oxide and prostaglandins and mediates vasodilation, natriuresis, diuresis, and oxidative stress. Thus, a reduced tone of the Ang-(1-7) system may contribute to these pathologies as well. Moreover, the non-classical RAS components may contribute to the effects of therapeutic blockade of the classical system to reduce blood pressure and attenuate various indices of renal injury. The review considers recent studies on the ACE2-Ang-(1-7)-Mas receptor axis regarding the precursor for Ang-(1-7), the intracellular expression and sex differences of this system, as well as an emerging role of the Ang1-(1-7) pathway in fetal programing events and cardiovascular dysfunction.
Keywords: ACE; ACE2; Ala1-Ang-(1–7); Ang-(1–7); Mas receptor; Mas-related receptor D; fetal programing.
Figures
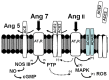
References
-
- Chappell MC, Brosnihan KB, Diz DI, Ferrario CM. Identification of angiotensin-(1-7) in rat brain: evidence for differential processing of angiotensin peptides. J Biol Chem (1989) 264:16518–23 - PubMed
-
- de Gasparo M, Catt KJ, Inagami T, Wright JW, Unger TH. The angiotensin II receptors. Pharmacol Rev (2000) 52:415–72 - PubMed
-
- Kambayashi Y, Bardhan S, Takahashi K, Tsuzuki S, Inui H, Hamakubo T, et al. Molecular cloning of a novel angiotensin II receptor isoform involved in phosphotyrosine phosphatase inhibition. J Biol Chem (1993) 268:24543–6 - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

