Regional gray matter volume is associated with empathizing and systemizing in young adults
- PMID: 24409308
- PMCID: PMC3883687
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0084782
Regional gray matter volume is associated with empathizing and systemizing in young adults
Abstract
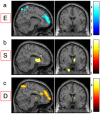
Empathizing is defined as the drive to identify the mental states of others for predicting their behavior and responding with an appropriate emotion. Systemizing is defined as the drive to analyze a system in terms of the rules that govern the system in order to predict its behavior. Using voxel-based morphometry and questionnaires in a large sample of normal, right-handed young adults, we investigated the regional gray matter volume (rGMV) correlates of empathizing and systemizing and additionally those of the D score, which is the difference between systemizing and empathizing, to reveal the comprehensive picture of those correlates. Negative rGMV correlates of empathizing and positive rGMV correlates of the D score (formed by the negative correlation between rGMV and empathizing), were found primarily in nodes in the default mode network, mirror neuron system, dorsal anterior cingulate cortex, and the lateral part of the prefrontal cortex together with other areas. Positive rGMV correlates of systemizing and of the D score (formed by the positive correlation between rGMV and systemizing) were found primarily in nodes in the external attention system, middle cingulate cortex, and other regions. Negative rGMV correlates of systemizing were found in an area close to the left posterior insula and putamen. These findings reconcile some previously inconsistent findings, provide other new findings and suggest that these areas contribute to empathizing-systemizing. Furthermore, the negative/positive rGMV correlates of empathizing and positive/negative rGMV correlates of systemizing overlapped substantially. This may be in line with the notion that empathizing and systemizing compete neurally in the brain.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Baron-Cohen S, Knickmeyer RC, Belmonte MK (2005) Sex differences in the brain: implications for explaining autism. Science 310: 819–823. - PubMed
-
- Wakabayashi A, Baron-Cohen S, Wheelwright S, Goldenfeld N, Delaney J, et al. (2006) Development of short forms of the Empathy Quotient (EQ-Short) and the Systemizing Quotient (SQ-Short). Personality and individual differences 41: 929–940.
-
- Baron-Cohen S, Wheelwright S (2004) The empathy quotient: an investigation of adults with Asperger syndrome or high functioning autism, and normal sex differences. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders 34: 163–175. - PubMed
-
- Wakabayashi A, Baron-Cohen S, Uchiyama T, Yoshida Y, Kuroda M, et al. (2007) Empathizing and systemizing in adults with and without autism spectrum conditions: cross-cultural stability. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders 37: 1823–1832. - PubMed
-
- Baron-Cohen S, Richler J, Bisarya D, Gurunathan N, Wheelwright S (2003) The systemizing quotient: an investigation of adults with Asperger syndrome or high-functioning autism, and normal sex differences. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London Series B: Biological Sciences 358: 361–374. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

