The applications of buckminsterfullerene C60 and derivatives in orthopaedic research
- PMID: 24409811
- PMCID: PMC4124742
- DOI: 10.3109/03008207.2013.877894
The applications of buckminsterfullerene C60 and derivatives in orthopaedic research
Abstract
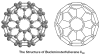
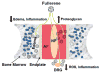
Abstract Buckminsterfullerene C60 and derivatives have been extensively explored in biomedical research due to their unique structure and unparalleled physicochemical properties. C60 is characterized as a "free radical sponge" with an anti-oxidant efficacy several hundred-fold higher than conventional anti-oxidants. Also, the C60 core has a strong electron-attracting ability and numerous functional compounds with widely different properties can be added to this fullerene cage. This review focused on the applications of C60 and derivatives in orthopaedic research, such as the treatment of cartilage degeneration, bone destruction, intervertebral disc degeneration (IVDD), vertebral bone marrow disorder, radiculopathy, etc., as well as their toxicity in vitro and in vivo. We suggest that C60 and derivatives, especially the C60 cores coupled with functional groups presenting new biological and pharmacological activities, are advantageous in orthopaedic research and will be promising in clinical performance for musculoskeletal disorders treatment; however, the pharmacokinetics and toxicology of these agents as local/systemic administration need to be carefully determined.
Conflict of interest statement
We thank the financial supports from NIH (R21AR57512) and NASS. The authors report no conflicts of interest. The authors alone are responsible for the content and writing of the paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Facile Low-Temperature Synthesis of Cellulose Nanocrystals Carrying Buckminsterfullerene and Its Radical Scavenging Property in Vitro.Biomacromolecules. 2017 Dec 11;18(12):4034-4040. doi: 10.1021/acs.biomac.7b01095. Epub 2017 Nov 22. Biomacromolecules. 2017. PMID: 29131597
-
Antioxidant action of sugar-pendant C60 fullerenes.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2009 Oct 15;19(20):5902-4. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2009.08.067. Epub 2009 Aug 21. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2009. PMID: 19736008
-
Fullerene C60 with cytoprotective and cytotoxic potential: prospects as a novel treatment agent in Dermatology?Exp Dermatol. 2017 Mar;26(3):220-224. doi: 10.1111/exd.13172. Epub 2017 Feb 2. Exp Dermatol. 2017. PMID: 27541937
-
Biological applications of hydrophilic C60 derivatives (hC60s)- a structural perspective.Eur J Med Chem. 2016 Jun 10;115:438-52. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2016.03.024. Epub 2016 Mar 11. Eur J Med Chem. 2016. PMID: 27049677 Review.
-
[Preparation and Evaluation of Fullerene Based Nanomedicine].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2019;139(12):1539-1546. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.19-00172. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2019. PMID: 31787641 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Nanoparticle fullerol alleviates radiculopathy via NLRP3 inflammasome and neuropeptides.Nanomedicine. 2017 Aug;13(6):2049-2059. doi: 10.1016/j.nano.2017.03.015. Epub 2017 Apr 9. Nanomedicine. 2017. PMID: 28404518 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial photodynamic inactivation in nanomedicine: small light strides against bad bugs.Nanomedicine (Lond). 2015;10(15):2379-404. doi: 10.2217/nnm.15.67. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2015. Retraction in: Nanomedicine (Lond). 2023 Mar;18(6):577. doi: 10.2217/nnm.15.67r1. PMID: 26305189 Free PMC article. Retracted. Review.
-
A Critical Appraisal of Functionalized 2-Dimensional Carbon-Based Nanomaterials for Drug Delivery Applications.Recent Pat Nanotechnol. 2024;18(4):479-493. doi: 10.2174/1872210518666230911150337. Recent Pat Nanotechnol. 2024. PMID: 37702173 Review.
-
C60 Fullerenes Suppress Reactive Oxygen Species Toxicity Damage in Boar Sperm.Nanomicro Lett. 2019 Nov 27;11(1):104. doi: 10.1007/s40820-019-0334-5. Nanomicro Lett. 2019. PMID: 34138040 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the Effects of Carbon 60 Nanoparticle Exposure to Adult Zebrafish: A Behavioral and Biochemical Approach to Elucidate the Mechanism of Toxicity.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Dec 3;19(12):3853. doi: 10.3390/ijms19123853. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30513951 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aschberger K, Johnston HJ, Stone V, Aitken RJ, Tran CL, Hankin SM, et al. Review of fullerene toxicity and exposure – appraisal of a human health risk assessment, based on open literature. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. 2010;58:455–73. - PubMed
-
- Kroto HW, Heath JR, Obrien SC, Curl RF, Smalley RE. C-60 – Buckminsterfullerene. Nature. 1985;318:162–3.
-
- Satoh M, Takayanagi I. Pharmacological studies on fullerene (C60), a novel carbon allotrope, and its derivatives. J Pharmacol Sci. 2006;100:513–18. - PubMed
-
- Krusic PJ, Wasserman E, Keizer PN, Morton JR, Preston KF. Radical reactions of c60. Science. 1991;254:1183–5. - PubMed
-
- Nielsen GD, Roursgaard M, Jensen KA, Poulsen SS, Larsen ST. In vivo biology and toxicology of fullerenes and their derivatives. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2008;103:197–208. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
