Optimising cardioprotection during myocardial ischaemia: targeting potential intracellular pathways with glucagon-like peptide-1
- PMID: 24410815
- PMCID: PMC3893610
- DOI: 10.1186/1475-2840-13-12
Optimising cardioprotection during myocardial ischaemia: targeting potential intracellular pathways with glucagon-like peptide-1
Abstract
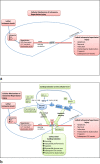
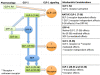
Coronary heart disease and type-2 diabetes are both major global health burdens associated with an increased risk of myocardial infarction (MI). Following MI, ischaemia-reperfusion injury (IRI) remains a significant contributor to myocardial injury at the cellular level. Research has focussed on identifying a strategy or intervention to minimise IRI to optimise reperfusion therapy, with the aim of delivering a superior clinical outcome. The incretin hormone glucagon-like peptide-1, already an established basis for the treatment of type-2 diabetes, also has the potential to protect against IRI. We explain the physiology and cellular processes involved in IRI, and the intracellular pathways activated by GLP-1, which could intercept IRI and deliver cardioprotection. The review also examines the current preclinical and clinical evidence for GLP-1 in cardioprotection and future directions for research as we look for an effective adjunctive treatment to minimise IRI.
Figures
References
-
- Frohlich GM, Meier P, White SK, Yellon DM, Hausenloy DJ. Myocardial reperfusion injury: looking beyond primary PCI. Eur Heart J. 2013;32(23):1714–1722. - PubMed
-
- Hausenloy DJ, Botker HE, Condorelli G, Ferdinandy P, Garcia-Dorado D, Heusch G, Lecour S, van Laake LW, Madonna R, Ruiz-Meana M. et al.Translating cardioprotection for patient benefit: position paper from the working group of cellular biology of the heart of the european society of cardiology. Cardiovasc Res. 2013;98(1):7–27. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvt004. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

