Coil design considerations for deep transcranial magnetic stimulation
- PMID: 24411523
- PMCID: PMC4020988
- DOI: 10.1016/j.clinph.2013.11.038
Coil design considerations for deep transcranial magnetic stimulation
Abstract
Objectives: To explore the field characteristics and design tradeoffs of coils for deep transcranial magnetic stimulation (dTMS).
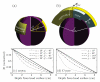
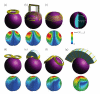
Methods: We simulated parametrically two dTMS coil designs on a spherical head model using the finite element method, and compare them with five commercial TMS coils, including two that are FDA approved for the treatment of depression (ferromagnetic-core figure-8 and H1 coil).
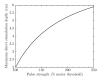
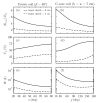
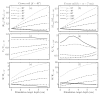
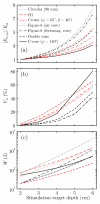
Results: Smaller coils have a focality advantage over larger coils; however, this advantage diminishes with increasing target depth. Smaller coils have the disadvantage of producing stronger field in the superficial cortex and requiring more energy. When the coil dimensions are large relative to the head size, the electric field decay in depth becomes linear, indicating that, at best, the electric field attenuation is directly proportional to the depth of the target. Ferromagnetic cores improve electrical efficiency for targeting superficial brain areas; however magnetic saturation reduces the effectiveness of the core for deeper targets, especially for highly focal coils. Distancing winding segments from the head, as in the H1 coil, increases the required stimulation energy.
Conclusions: Among standard commercial coils, the double cone coil offers high energy efficiency and balance between stimulated volume and superficial field strength. Direct TMS of targets at depths of ~4 cm or more results in superficial stimulation strength that exceeds the upper limit in current rTMS safety guidelines. Approaching depths of ~6 cm is almost certainly unsafe considering the excessive superficial stimulation strength and activated brain volume.
Significance: Coil design limitations and tradeoffs are important for rational and safe exploration of dTMS.
Keywords: Deep transcranial magnetic stimulation; Electric field; Energy; Focality; Model.
Copyright © 2013 International Federation of Clinical Neurophysiology. Published by Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
Comment in
-
Promise and perspective in transcranial magnetic stimulation.Clin Neurophysiol. 2014 Jun;125(6):1077-8. doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2013.12.097. Epub 2013 Dec 21. Clin Neurophysiol. 2014. PMID: 24412333 No abstract available.
-
Realistic shape head model and spherical model as methods for TMS coil characterization.Clin Neurophysiol. 2015 Jul;126(7):1455-6. doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2014.08.027. Epub 2014 Oct 28. Clin Neurophysiol. 2015. PMID: 25468236 No abstract available.
-
On the characterization of coils for deep transcranial magnetic stimulation.Clin Neurophysiol. 2015 Jul;126(7):1456-7. doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2014.10.144. Epub 2014 Oct 28. Clin Neurophysiol. 2015. PMID: 25468237 No abstract available.
References
-
- Agnew WF, McCreery DB. Considerations for safety in the use of extracranial stimulation for motor evoked potentials. Neurosurgery. 1987;20:143–147. - PubMed
-
- Al-Mutawaly N, de Bruin H, Findlay RD. Magnetic nerve stimulation: field focality and depth of penetration. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2001;ume 1:877–880.
-
- Balslev D, Braet W, McAllister C, Miall RC. Inter-individual variability in optimal current direction for transcranial magnetic stimulation of the motor cortex. J Neurosci Methods. 2007;162:309–313. - PubMed
-
- Bersani FS, Girardi N, Sanna L, Mazzarini L, Santucci C, Kotzalidis GD, et al. Deep transcranial magnetic stimulation for treatment-resistant bipolar depression: a case report of acute and maintenance efficacy. Neurocase. 2012 In press:doi:10.1080/13554794.2012.690429. - PubMed
-
- Bersani FS, Minichino A, Enticott PG, Mazzarini L, Khan N, Antonacci G, et al. Deep transcranial magnetic stimulation as a treatment for psychiatric disorders: a comprehensive review. Eur Psychiatry. 2013;28:30–39. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

