Increasing value and reducing waste: addressing inaccessible research
- PMID: 24411650
- PMCID: PMC4533904
- DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)62296-5
Increasing value and reducing waste: addressing inaccessible research
Abstract
The methods and results of health research are documented in study protocols, full study reports (detailing all analyses), journal reports, and participant-level datasets. However, protocols, full study reports, and participant-level datasets are rarely available, and journal reports are available for only half of all studies and are plagued by selective reporting of methods and results. Furthermore, information provided in study protocols and reports varies in quality and is often incomplete. When full information about studies is inaccessible, billions of dollars in investment are wasted, bias is introduced, and research and care of patients are detrimentally affected. To help to improve this situation at a systemic level, three main actions are warranted. First, academic institutions and funders should reward investigators who fully disseminate their research protocols, reports, and participant-level datasets. Second, standards for the content of protocols and full study reports and for data sharing practices should be rigorously developed and adopted for all types of health research. Finally, journals, funders, sponsors, research ethics committees, regulators, and legislators should endorse and enforce policies supporting study registration and wide availability of journal reports, full study reports, and participant-level datasets.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

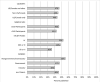
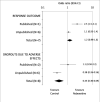
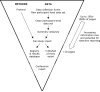
Comment in
-
Research: increasing value, reducing waste.Lancet. 2014 Mar 29;383(9923):1124. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)60559-6. Lancet. 2014. PMID: 24679622 No abstract available.
-
Research: increasing value, reducing waste - Authors' reply.Lancet. 2014 Mar 29;383(9923):1126-7. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)60563-8. Lancet. 2014. PMID: 24679627 No abstract available.
-
Review and publication of protocol submissions to Trials - what have we learned in 10 years?Trials. 2016 Dec 16;18(1):34. doi: 10.1186/s13063-016-1743-0. Trials. 2016. PMID: 28114958 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chalmers I. Underreporting research is scientific misconduct. JAMA. 1990;263:1405–8. - PubMed
-
- Song F, Parekh S, Hooper L, Loke YK, Ryder J, Sutton AJ, et al. Dissemination and publication of research findings: an updated review of related biases. Health Technol Assess. 2010;14:iii–193. - PubMed
-
- Røttingen JA, Regmi S, Eide M, Young AJ, Viergever RF, Ardal C, et al. Mapping of available health research and development data: what's there, what's missing, and what role is there for a global observatory? Lancet. 2013;382:1286–307. - PubMed
-
- Galsworthy MJ, Hristovski D, Lusa L, Ernst K, Irwin R, Charlesworth K, et al. The academic output of nine years of EU investment into health research. Lancet. 2012;380:971–2. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

