CKD of unknown origin in Central America: the case for a Mesoamerican nephropathy
- PMID: 24412050
- PMCID: PMC7115712
- DOI: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2013.10.062
CKD of unknown origin in Central America: the case for a Mesoamerican nephropathy
Abstract
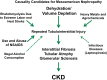
An epidemic of chronic kidney disease of unknown origin has emerged in the last decade in Central America and has been named Mesoamerican nephropathy. This form of chronic kidney disease is present primarily in young male agricultural workers from communities along the Pacific coast, especially workers in the sugarcane fields. In general, these men have a history of manual labor under very hot conditions in agricultural fields. Clinically, they usually present with normal or mildly elevated systemic blood pressure, asymptomatic yet progressive reduction in estimated glomerular filtration rate, low-grade non-nephrotic proteinuria, and often hyperuricemia and or hypokalemia. Diabetes is absent in this population. Kidney biopsies that have been performed show a chronic tubulointerstitial disease with associated secondary glomerulosclerosis and some signs of glomerular ischemia. The cause of the disease is unknown; this article discusses and analyzes some of the etiologic possibilities currently under consideration. It is relevant to highlight that recurrent dehydration is suggested in multiple studies, a condition that possibly could be exacerbated in some cases by other conditions, including the use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents. At present, Mesoamerican nephropathy is a medical enigma yet to be solved.
Keywords: Chronic kidney disease; Mesoamerica.
Copyright © 2014 National Kidney Foundation, Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Comment in
-
Pesticides and the epidemic of CKD in Central America.Am J Kidney Dis. 2014 Sep;64(3):477. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2014.03.022. Am J Kidney Dis. 2014. PMID: 25150854 No abstract available.
-
In reply to 'Pesticides and the epidemic of CKD in Central America'.Am J Kidney Dis. 2014 Sep;64(3):477-8. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2014.07.001. Am J Kidney Dis. 2014. PMID: 25150855 No abstract available.
References
-
- Drosten C., Günther S., Preiser W. Identification of a novel coronavirus in patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2003;348(20):1967–1976. - PubMed
-
- Perez-Padilla R., de la Rosa-Zamboni D., Ponce de Leon S., for the INER Working Group on Influenza Pneumonia and respiratory failure from swine-origin influenza A (H1N1) in Mexico. N Engl J Med. 2009;361(7):680–989. - PubMed
-
- Liu D., Shi W., Shi Y. Origin and diversity of novel avian influenza A H7N9 viruses causing human infection: phylogenetic, structural, and coalescent analyses. Lancet. 2013;381(9881):1926–1932. - PubMed
-
- Hranjec T., Kovac A., Kos J. Endemic nephropathy: the case for chronic poisoning by Aristolochia. Croat Med J. 2005;46(1):116–125. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous