Induction of innate lymphoid cell-derived interleukin-22 by the transcription factor STAT3 mediates protection against intestinal infection
- PMID: 24412612
- PMCID: PMC3919552
- DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2013.10.021
Induction of innate lymphoid cell-derived interleukin-22 by the transcription factor STAT3 mediates protection against intestinal infection
Abstract
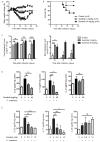
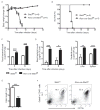
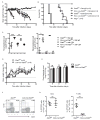
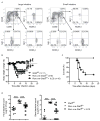
Inhibitors of the transcription factor STAT3 target STAT3-dependent tumorigenesis but patients often develop diarrhea from unknown mechanisms. Here we showed that STAT3 deficiency increased morbidity and mortality after Citrobacter rodentium infection with decreased secretion of cytokines including IL-17 and IL-22 associated with the transcription factor RORγt. Administration of the cytokine IL-22 was sufficient to rescue STAT3-deficient mice from lethal infection. Although STAT3 was required for IL-22 production in both innate and adaptive arms, by using conditional gene-deficient mice, we observed that STAT3 expression in RORγt(+) innate lymphoid cells (ILC3s), but not T cells, was essential for the protection. However, STAT3 was required for RORγt expression in T helper cells, but not in ILC3s. Activated STAT3 could directly bind to the Il22 locus. Thus, cancer therapies that utilize STAT3 inhibitors increase the risk for pathogen-mediated diarrhea through direct suppression of IL-22 from gut ILCs.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The aryl hydrocarbon receptor regulates gut immunity through modulation of innate lymphoid cells.Immunity. 2012 Jan 27;36(1):92-104. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2011.11.011. Epub 2011 Dec 15. Immunity. 2012. PMID: 22177117 Free PMC article.
-
Microbial flora drives interleukin 22 production in intestinal NKp46+ cells that provide innate mucosal immune defense.Immunity. 2008 Dec 19;29(6):958-70. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2008.11.001. Epub 2008 Dec 11. Immunity. 2008. PMID: 19084435
-
DOCK8 regulates protective immunity by controlling the function and survival of RORγt+ ILCs.Nat Commun. 2014 Aug 5;5:4603. doi: 10.1038/ncomms5603. Nat Commun. 2014. PMID: 25091235 Free PMC article.
-
Heterogeneity and diversity of group 3 innate lymphoid cells: new cells on the block.Int Immunol. 2016 Jan;28(1):29-34. doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxv054. Epub 2015 Oct 13. Int Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26462712 Review.
-
Group 3 innate lymphoid cells (ILC3s): Origin, differentiation, and plasticity in humans and mice.Eur J Immunol. 2015 Aug;45(8):2171-82. doi: 10.1002/eji.201545598. Epub 2015 Jun 18. Eur J Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26031799 Review.
Cited by
-
Gut Bacteria Induce Granzyme B Expression in Human Colonic ILC3s In Vitro in an IL-15-Dependent Manner.J Immunol. 2021 Jun 15;206(12):3043-3052. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2000239. Epub 2021 Jun 11. J Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34117105 Free PMC article.
-
Coordination of Mucosal Immunity by Innate Lymphoid Cells.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2022;1365:113-134. doi: 10.1007/978-981-16-8387-9_8. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2022. PMID: 35567744
-
Interleukin-7 Receptor Alpha in Innate Lymphoid Cells: More Than a Marker.Front Immunol. 2019 Dec 11;10:2897. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02897. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31921158 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vitamin D/Vitamin D Receptor Signaling Is Required for Normal Development and Function of Group 3 Innate Lymphoid Cells in the Gut.iScience. 2019 Jul 26;17:119-131. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2019.06.026. Epub 2019 Jun 20. iScience. 2019. PMID: 31272068 Free PMC article.
-
Innate Lymphoid Cells: A Link between the Nervous System and Microbiota in Intestinal Networks.Mediators Inflamm. 2019 Jan 20;2019:1978094. doi: 10.1155/2019/1978094. eCollection 2019. Mediators Inflamm. 2019. PMID: 30804706 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bry L, Brenner MB. Critical role of T cell-dependent serum antibody, but not the gut-associated lymphoid tissue, for surviving acute mucosal infection with Citrobacter rodentium, an attaching and effacing pathogen. J Immunol. 2004;172:433–441. - PubMed
-
- Eberl G. Development and evolution of RORgammat+ cells in a microbe’s world. Immunol Rev. 2012;245:177–188. - PubMed
-
- Eberl G, Littman DR. Thymic origin of intestinal alphabeta T cells revealed by fate mapping of RORgammat+ cells. Science. 2004;305:248–251. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

