c-Abl phosphorylates α-synuclein and regulates its degradation: implication for α-synuclein clearance and contribution to the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease
- PMID: 24412932
- PMCID: PMC4014189
- DOI: 10.1093/hmg/ddt674
c-Abl phosphorylates α-synuclein and regulates its degradation: implication for α-synuclein clearance and contribution to the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease
Abstract
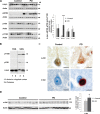
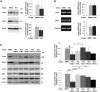
Increasing evidence suggests that the c-Abl protein tyrosine kinase could play a role in the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease (PD) and other neurodegenerative disorders. c-Abl has been shown to regulate the degradation of two proteins implicated in the pathogenesis of PD, parkin and α-synuclein (α-syn). The inhibition of parkin's neuroprotective functions is regulated by c-Abl-mediated phosphorylation of parkin. However, the molecular mechanisms by which c-Abl activity regulates α-syn toxicity and clearance remain unknown. Herein, using NMR spectroscopy, mass spectrometry, in vitro enzymatic assays and cell-based studies, we established that α-syn is a bona fide substrate for c-Abl. In vitro studies demonstrate that c-Abl directly interacts with α-syn and catalyzes its phosphorylation mainly at tyrosine 39 (pY39) and to a lesser extent at tyrosine 125 (pY125). Analysis of human brain tissues showed that pY39 α-syn is detected in the brains of healthy individuals and those with PD. However, only c-Abl protein levels were found to be upregulated in PD brains. Interestingly, nilotinib, a specific inhibitor of c-Abl kinase activity, induces α-syn protein degradation via the autophagy and proteasome pathways, whereas the overexpression of α-syn in the rat midbrains enhances c-Abl expression. Together, these data suggest that changes in c-Abl expression, activation and/or c-Abl-mediated phosphorylation of Y39 play a role in regulating α-syn clearance and contribute to the pathogenesis of PD.
Figures








References
-
- Moresco E.M., Koleske A.J. Regulation of neuronal morphogenesis and synaptic function by Abl family kinases. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2003;13:535–544. - PubMed
-
- Zukerberg L.R., Patrick G.N., Nikolic M., Humbert S., Wu C.L., Lanier L.M., Gertler F.B., Vidal M., Van Etten R.A., Tsai L.H. Cables links Cdk5 and c-Abl and facilitates Cdk5 tyrosine phosphorylation, kinase upregulation, and neurite outgrowth. Neuron. 2000;26:633–646. - PubMed
-
- Lanier L.M., Gertler F.B. From Abl to actin: Abl tyrosine kinase and associated proteins in growth cone motility. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2000;10:80–87. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

