Improved oxygenation 24 hours after transition to airway pressure release ventilation or high-frequency oscillatory ventilation accurately discriminates survival in immunocompromised pediatric patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome*
- PMID: 24413319
- PMCID: PMC4114308
- DOI: 10.1097/PCC.0000000000000069
Improved oxygenation 24 hours after transition to airway pressure release ventilation or high-frequency oscillatory ventilation accurately discriminates survival in immunocompromised pediatric patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome*
Abstract
Objectives: Children with an immunocompromised condition and requiring invasive mechanical ventilation have high risk of death. Such patients are commonly transitioned to rescue modes of nonconventional ventilation, including airway pressure release ventilation and high-frequency oscillatory ventilation, for acute respiratory distress syndrome refractory to conventional ventilation. Our aim was to describe our experience with airway pressure release ventilation and high-frequency oscillatory ventilation in children with an immunocompromised condition and acute respiratory distress syndrome refractory to conventional ventilation and to identify factors associated with survival.
Design: Retrospective cohort study.
Setting: Tertiary care, university-affiliated PICU.
Patients: Sixty pediatric patients with an immunocompromised condition and acute respiratory distress syndrome refractory to conventional ventilation transitioned to either airway pressure release ventilation or high-frequency oscillatory ventilation.
Interventions: None.
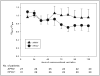
Measurements and main results: Demographic data, ventilator settings, arterial blood gases, oxygenation index, and PaO(2)/FIO(2) were recorded before transition to either mode of nonconventional ventilation and at predetermined intervals after transition for up to 5 days. Mortality in the entire cohort was 63% and did not differ between patients transitioned to airway pressure release ventilation and high-frequency oscillatory ventilation. For both airway pressure release ventilation and high-frequency oscillatory ventilation, improvements in oxygenation index and PaO(2)/FIO(2) at 24 hours expressed as a fraction of pretransition values (oxygenation index(24)/oxygenation index(pre) and PaO(2)/FIO(224)/PaO(2)/FIO(2pre)) reliably discriminated nonsurvivors from survivors, with receiver operating characteristic areas under the curves between 0.89 and 0.95 (p for all curves < 0.001). Sensitivity-specificity analysis suggested that less than 15% reduction in oxygenation index (90% sensitive, 75% specific) or less than 90% increase in PaO(2)/FIO(2) (80% sensitive, 94% specific) 24 hours after transition to airway pressure release ventilation were the optimal cutoffs to identify nonsurvivors. The comparable values 24 hours after transition to high-frequency oscillatory ventilation were less than 5% reduction in oxygenation index (100% sensitive, 83% specific) or less than 80% increase in PaO(2)/FIO(2) (91% sensitive, 89% specific) to identify nonsurvivors.
Conclusions: In this single-center retrospective study of pediatric patients with an immunocompromised condition and acute respiratory distress syndrome failing conventional ventilation transitioned to either airway pressure release ventilation or high-frequency oscillatory ventilation, improved oxygenation at 24 hours expressed as PaO(2)/FIO(224)/PaO(2)/FIO(2pre) or oxygenation index(24)/oxygenation indexpre reliably discriminates nonsurvivors from survivors. These findings should be prospectively verified.
Figures


Comment in
-
Immunocompromised patients and ventilation support: new treatment perspectives and prognosis for applied modes of ventilation*.Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2014 May;15(4):379-80. doi: 10.1097/PCC.0000000000000084. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2014. PMID: 24801423 No abstract available.
References
-
- Bratton SL, Van Duker H, Statler KD, et al. Lower hospital mortality and complications after pediatric hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Crit Care Med. 2008;36:923–927. - PubMed
-
- Duncan CN, Lehmann LE, Cheifetz IM, et al. Pediatric Acute Lung Injury and Sepsis (PALISI) Network. Clinical outcomes of children receiving intensive cardiopulmonary support during hematopoietic stem cell transplant. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2013;14:261–267. - PubMed
-
- Piastra M, De Luca D, Pietrini D, et al. Noninvasive pressure-support ventilation in immunocompromised children with ARDS: A feasibility study. Intensive Care Med. 2009;35:1420–1427. - PubMed
-
- Arnold JH, Anas NG, Luckett P, et al. High-frequency oscillatory ventilation in pediatric respiratory failure: A multicenter experience. Crit Care Med. 2000;28:3913–3919. - PubMed
-
- Willson DF, Thomas NJ, Markovitz BP, et al. Pediatric Acute Lung Injury and Sepsis Investigators. Effect of exogenous surfactant (calfactant) in pediatric acute lung injury: A randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2005;293:470–476. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

