T-type channels buddy up
- PMID: 24413887
- PMCID: PMC3951889
- DOI: 10.1007/s00424-013-1434-6
T-type channels buddy up
Abstract
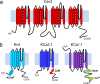
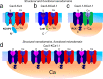
The electrical output of neurons relies critically on voltage- and calcium-gated ion channels. The traditional view of ion channels is that they operate independently of each other in the plasma membrane in a manner that could be predicted according to biophysical characteristics of the isolated current. However, there is increasing evidence that channels interact with each other not just functionally but also physically. This is exemplified in the case of Cav3 T-type calcium channels, where new work indicates the ability to form signaling complexes with different types of calcium-gated and even voltage-gated potassium channels. The formation of a Cav3-K complex provides the calcium source required to activate KCa1.1 or KCa3.1 channels and, furthermore, to bestow a calcium-dependent regulation of Kv4 channels via associated KChIP proteins. Here, we review these interactions and discuss their significance in the context of neuronal firing properties.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Regulation of neuronal activity by Cav3-Kv4 channel signaling complexes.Nat Neurosci. 2010 Mar;13(3):333-7. doi: 10.1038/nn.2493. Epub 2010 Feb 14. Nat Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20154682
-
Calcium-gated K+ channels of the KCa1.1- and KCa3.1-type couple intracellular Ca2+ signals to membrane hyperpolarization in mesenchymal stromal cells from the human adipose tissue.Pflugers Arch. 2017 Feb;469(2):349-362. doi: 10.1007/s00424-016-1932-4. Epub 2016 Dec 27. Pflugers Arch. 2017. PMID: 28028617
-
Low voltage activation of KCa1.1 current by Cav3-KCa1.1 complexes.PLoS One. 2013 Apr 23;8(4):e61844. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0061844. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23626738 Free PMC article.
-
Signal processing by T-type calcium channel interactions in the cerebellum.Front Cell Neurosci. 2013 Nov 27;7:230. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2013.00230. Front Cell Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 24348329 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Functional specificity of T-type calcium channels and their roles in neuronal differentiation].J Soc Biol. 2003;197(3):235-47. J Soc Biol. 2003. PMID: 14708345 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Mutant huntingtin enhances activation of dendritic Kv4 K+ channels in striatal spiny projection neurons.Elife. 2019 Apr 24;8:e40818. doi: 10.7554/eLife.40818. Elife. 2019. PMID: 31017573 Free PMC article.
-
A Cav3.2/Stac1 molecular complex controls T-type channel expression at the plasma membrane.Channels (Austin). 2016 Sep 2;10(5):346-354. doi: 10.1080/19336950.2016.1186318. Epub 2016 May 5. Channels (Austin). 2016. PMID: 27149520 Free PMC article.
-
T-types make your clock tick.J Physiol. 2015 Feb 15;593(4):757-8. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2014.288423. J Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25708917 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Modulation of Low-Voltage-Activated Inward Current Permeable to Sodium and Calcium by DARPP-32 Drives Spontaneous Firing of Insect Octopaminergic Neurosecretory Cells.Front Syst Neurosci. 2017 May 19;11:31. doi: 10.3389/fnsys.2017.00031. eCollection 2017. Front Syst Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28579948 Free PMC article.
-
Glycans and Carbohydrate-Binding/Transforming Proteins in Axon Physiology.Adv Neurobiol. 2023;29:185-217. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-12390-0_7. Adv Neurobiol. 2023. PMID: 36255676
References
-
- Adelman JP, Maylie J, Sah P. Small-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channels: form and function. Annu Rev Physiol. 2012;74:245–269. - PubMed
-
- An WF, et al. Modulation of A-type potassium channels by a family of calcium sensors. Nature. 2000;403:553–556. - PubMed
-
- Anderson D, et al. Regulation of neuronal activity by Cav3–Kv4 channel signaling complexes. Nat Neurosci. 2010;13:333–337. - PubMed
-
- Anderson D, Rehak R, Hameed S, Mehaffey WH, Zamponi GW, Turner RW. Regulation of the K(V)4.2 complex by Ca(V)3.1 calcium channels. Channels (Austin) 2010;4(3):163–167. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

