Altered inflammatory responses to Citrobacter rodentium infection, but not bacterial lipopolysaccharide, in mice lacking the Cyp4a10 or Cyp4a14 genes
- PMID: 24413902
- PMCID: PMC4035451
- DOI: 10.1007/s10753-013-9809-6
Altered inflammatory responses to Citrobacter rodentium infection, but not bacterial lipopolysaccharide, in mice lacking the Cyp4a10 or Cyp4a14 genes
Abstract
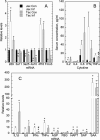
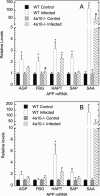
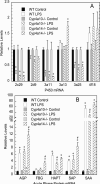
Murine hepatic Cyp4a mRNAs are markedly downregulated during inflammation. Here, we investigated the roles of Cyp4a10 and Cyp4a14 in the response to infection with C. rodentium. Absence of either Cyp4a gene attenuated or abrogated the changes in spleen weight, colon crypt length, hepatic cytokine, and acute phase protein mRNAs, and serum acute phase proteins and cytokines caused by infection. Cyp4a10(-/-) mice on a low-salt diet had a similar hepatic acute phase response as those mice on a high-salt diet, suggesting that hypertension associated with this genotype is not the cause of their altered inflammatory response. In contrast, wild-type, Cyp4a10(-/-), and Cyp4a14(-/-) mice showed similar responses to injected LPS. These results implicate Cyp4a10 and Cyp4a14 in the regulation of the host inflammatory response to enteropathogenic bacterial infection but not to acute aseptic inflammation. Understanding the mechanism of this role may lead to novel therapeutic approaches in some inflammatory diseases.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Selective modulation of hepatic cytochrome P450 and flavin monooxygenase 3 expression during citrobacter rodentium infection in severe combined immune-deficient mice.Drug Metab Dispos. 2012 Oct;40(10):1894-9. doi: 10.1124/dmd.112.046557. Epub 2012 Jun 27. Drug Metab Dispos. 2012. PMID: 22745333 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatic and renal cytochrome p450 gene regulation during citrobacter rodentium infection in wild-type and toll-like receptor 4 mutant mice.Drug Metab Dispos. 2006 Mar;34(3):354-60. doi: 10.1124/dmd.105.007393. Epub 2005 Dec 8. Drug Metab Dispos. 2006. PMID: 16339354 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of hepatic cytochrome P450 expression in mice with intestinal or systemic infections of citrobacter rodentium.Drug Metab Dispos. 2009 Feb;37(2):366-74. doi: 10.1124/dmd.108.024240. Epub 2008 Oct 29. Drug Metab Dispos. 2009. PMID: 18971315 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of hepatic cytochrome P450s by Citrobacter rodentium infection in interleukin-6- and interferon-{gamma}-null mice.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2010 Nov;335(2):480-8. doi: 10.1124/jpet.110.171488. Epub 2010 Aug 18. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2010. PMID: 20719939 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of cytochrome P-450 gene expression in endotoxemic mice is tissue specific and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha dependent.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1999 Sep;290(3):1250-7. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1999. PMID: 10454501
Cited by
-
Gut Microbiota Deficiency Exacerbates Liver Injury in Bile Duct Ligated Mice via Inflammation and Lipid Metabolism.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 6;24(4):3180. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043180. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36834588 Free PMC article.
-
Defining Host Responses during Systemic Bacterial Infection through Construction of a Murine Organ Proteome Atlas.Cell Syst. 2018 May 23;6(5):579-592.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.cels.2018.04.010. Epub 2018 May 16. Cell Syst. 2018. PMID: 29778837 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-omics analysis explores the effect of chronic exercise on liver metabolic reprogramming in mice.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Jun 20;11:1199902. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1199902. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 37408533 Free PMC article.
-
Mice Fed a High-Fat Diet Supplemented with Resistant Starch Display Marked Shifts in the Liver Metabolome Concurrent with Altered Gut Bacteria.J Nutr. 2016 Dec;146(12):2476-2490. doi: 10.3945/jn.116.238931. Epub 2016 Nov 2. J Nutr. 2016. PMID: 27807042 Free PMC article.
-
Reducing Oxidative Stress-Mediated Alcoholic Liver Injury by Multiplexed RNAi of Cyp2e1, Cyp4a10, and Cyp4a14.Biomedicines. 2024 Jul 6;12(7):1505. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12071505. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39062078 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hardwick JP. Cytochrome P450 omega hydroxylase (CYP4) function in fatty acid metabolism and metabolic diseases. Biochemical Pharmacology. 2008;75:2263–2275. - PubMed
-
- Johnson EF, Palmer CN, Griffin KJ, Hsu MH. Role of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor in cytochrome P450 4A gene regulation. FASEB journal. 1996;10:1241–1248. - PubMed
-
- Sanders RJ, Ofman R, Valianpour F, Kemp S, Wanders RJ. Evidence for two enzymatic pathways for omega-oxidation of docosanoic acid in rat liver microsomes. Journal of Lipid Research. 2005;46:1001–1008. - PubMed
-
- Gainer JV, Bellamine A, Dawson EP, Womble KE, Grant SW, Wang Y, Cupples LA, Guo CY, Demissie S, O'Donnell CJ, Brown NJ, Waterman MR, Capdevila JH. Functional variant of CYP4A11 20-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid synthase is associated with essential hypertension. Circulation. 2005;111:63–69. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

