A case of neurotoxicity following envenomation by the Sidewinder rattlesnake, Crotalus cerastes
- PMID: 24414250
- PMCID: PMC4057548
- DOI: 10.1007/s13181-013-0373-0
A case of neurotoxicity following envenomation by the Sidewinder rattlesnake, Crotalus cerastes
Abstract
Introduction: North American rattlesnake envenomations typically result in local tissue injury and hematologic derangements. Neurotoxicity is uncommon but when present often manifests as fasciculations and paresthesias. Neurotoxicity following Sidewinder (Crotalus cerastes) envenomation has not been previously reported.
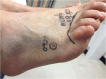
Case report: A 56-year-old man bitten on the right foot developed painful paresthesias, weakness and fasciculations of the right lower extremity, and involuntary muscle contractions of the anterior thigh. Local tissue effects and hemotoxicity never developed. The patient was discharged 5 days after the bite with resolution of fasciculations but continued to have right-sided weakness. The snake was identified as a Sidewinder, C. cerastes, by the patient and two independent herpetologists.
Conclusion: This is the first reported case of a Sidewinder rattlesnake envenomation resulting in neurotoxicity.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources