Enhanced lysis and accelerated establishment of viscoelastic properties of fibrin clots are associated with pulmonary embolism
- PMID: 24414255
- PMCID: PMC3949054
- DOI: 10.1152/ajplung.00265.2013
Enhanced lysis and accelerated establishment of viscoelastic properties of fibrin clots are associated with pulmonary embolism
Abstract
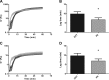
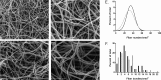
The factors that contribute to pulmonary embolism (PE), a potentially fatal complication of deep vein thrombosis (DVT), remain poorly understood. Whereas fibrin clot structure and functional properties have been implicated in the pathology of venous thromboembolism and the risk for cardiovascular complications, their significance in PE remains uncertain. Therefore, we systematically compared and quantified clot formation and lysis time, plasminogen levels, viscoelastic properties, activated factor XIII cross-linking, and fibrin clot structure in isolated DVT and PE subjects. Clots made from plasma of PE subjects showed faster clot lysis times with no differences in lag time, rate of clot formation, or maximum absorbance of turbidity compared with DVT. Differences in lysis times were not due to alterations in plasminogen levels. Compared with DVT, clots derived from PE subjects showed accelerated establishment of viscoelastic properties, documented by a decrease in lag time and an increase in the rate of viscoelastic property formation. The rate and extent of fibrin cross-linking by activated factor XIII were similar between clots from DVT and PE subjects. Electron microscopy revealed that plasma fibrin clots from PE subjects exhibited lower fiber density compared with those from DVT subjects. These data suggest that clot structure and functional properties differ between DVT and PE subjects and provide insights into mechanisms that may regulate embolization.
Keywords: deep vein thrombosis; fibrin; lysis; pulmonary embolism.
Figures


References
-
- Anderson FA, Jr, Wheeler HB, Goldberg RJ, Hosmer DW, Patwardhan NA, Jovanovic B, Forcier A, Dalen JE. A population-based perspective of the hospital incidence and case-fatality rates of deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. The Worcester DVT Study. Arch Intern Med 151: 933–938, 1991 - PubMed
-
- Carr ME, Jr, Hermans J. Size and density of fibrin fibers from turbidity. Macromolecules 11: 46–50, 1978 - PubMed
-
- Collet JP, Allali Y, Lesty C, Tanguy ML, Silvain J, Ankri A, Blanchet B, Dumaine R, Gianetti J, Payot L, Weisel JW, Montalescot G. Altered fibrin architecture is associated with hypofibrinolysis and premature coronary atherothrombosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 26: 2567–2573, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Collet JP, Park D, Lesty C, Soria J, Soria C, Montalescot G, Weisel JW. Influence of fibrin network conformation and fibrin fiber diameter on fibrinolysis speed: dynamic and structural approaches by confocal microscopy. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 20: 1354–1361, 2000 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

