Long-term immune responses to vaccination in HIV-infected patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 24415637
- PMCID: PMC4761378
- DOI: 10.1093/cid/cit937
Long-term immune responses to vaccination in HIV-infected patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Vaccine-induced antibodies may wane more quickly in persons living with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) than in healthy individuals. We reviewed the literature on vaccines routinely recommended in HIV-infected patients to estimate how seroprotection decreases over time in those who initially responded to immunization. For each study retrieved from the literature, the decrease of seroprotection was modeled with a log binomial generalized linear model, and data were pooled in a meta-analysis to provide estimates of seroprotection 2 and 5 years after the last vaccine administration. Our analyses confirmed that the duration of seroprotection was shorter in HIV-infected patients and that with current guidelines, a substantial proportion of patients would have lost protective antibodies before a booster was proposed. We therefore discuss the implications for the monitoring of antibody levels and timing of revaccination in these patients.
Keywords: HIV; meta-analysis; vaccination.
Conflict of interest statement
SK, CT, FB, and PYB declare no conflicts of interest.
OL, TH reported not having shares or paid employment with pharmaceutical companies, being investigators on studies sponsored by different pharmaceutical companies.
Figures

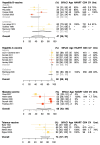

References
-
- Geretti AM, Doyle T. Immunization for HIV-positive individuals. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2010;23:32–38. - PubMed
-
- Abzug MJ. Vaccination in the immunocompromised child: a probe of immune reconstitution. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2009;28:233–236. - PubMed
-
- Siber GR, Chang I, Baker S, et al. Estimating the protective concentration of anti-pneumococcal capsular polysaccharide antibodies. Vaccine. 2007;25:3816–3826. - PubMed
-
- Abzug MJ, Song L-Y, Fenton T, et al. Pertussis booster vaccination in HIV-infected children receiving highly active antiretroviral therapy. Pediatrics. 2007;120:e1190–1202. - PubMed
-
- Gibb D, Giacomelli A, Masters J, et al. Persistence of antibody responses to Haemophilus influenzae type b polysaccharide conjugate vaccine in children with vertically acquired human immunodeficiency virus infection. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1996;15:1097–1101. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

