Lipoteichoic acids, phosphate-containing polymers in the envelope of gram-positive bacteria
- PMID: 24415723
- PMCID: PMC3957714
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.01155-13
Lipoteichoic acids, phosphate-containing polymers in the envelope of gram-positive bacteria
Abstract
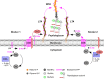
Lipoteichoic acids (LTA) are polymers of alternating units of a polyhydroxy alkane, including glycerol and ribitol, and phosphoric acid, joined to form phosphodiester units that are found in the envelope of Gram-positive bacteria. Here we review four different types of LTA that can be distinguished on the basis of their chemical structure and describe recent advances in the biosynthesis pathway for type I LTA, d-alanylated polyglycerol-phosphate linked to di-glucosyl-diacylglycerol. The physiological functions of type I LTA are discussed in the context of inhibitors that block their synthesis and of mutants with discrete synthesis defects. Research on LTA structure and function represents a large frontier that has been investigated in only few Gram-positive bacteria.
Figures



References
-
- Leloir LF, Cardini CE. 1957. Biosynthesis of glycogen from uridine diphosphate glucose. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 79:6340–6341. 10.1021/ja01580a061 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

