Immunopathology of inflammatory bowel disease
- PMID: 24415853
- PMCID: PMC3886033
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i1.6
Immunopathology of inflammatory bowel disease
Abstract
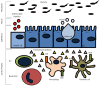
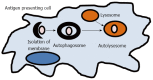
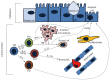
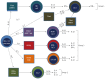
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) results from a complex series of interactions between susceptibility genes, the environment, and the immune system. The host microbiome, as well as viruses and fungi, play important roles in the development of IBD either by causing inflammation directly or indirectly through an altered immune system. New technologies have allowed researchers to be able to quantify the various components of the microbiome, which will allow for future developments in the etiology of IBD. Various components of the mucosal immune system are implicated in the pathogenesis of IBD and include intestinal epithelial cells, innate lymphoid cells, cells of the innate (macrophages/monocytes, neutrophils, and dendritic cells) and adaptive (T-cells and B-cells) immune system, and their secreted mediators (cytokines and chemokines). Either a mucosal susceptibility or defect in sampling of gut luminal antigen, possibly through the process of autophagy, leads to activation of innate immune response that may be mediated by enhanced toll-like receptor activity. The antigen presenting cells then mediate the differentiation of naïve T-cells into effector T helper (Th) cells, including Th1, Th2, and Th17, which alter gut homeostasis and lead to IBD. In this review, the effects of these components in the immunopathogenesis of IBD will be discussed.
Keywords: Adaptive immune system; Autophagy; Crohn’s disease; Inflammatory bowel disease; Innate immune system; Innate lymphoid cells; Microbiome; T helper 17; TL1A; Ulcerative colitis.
Figures
References
-
- Lichtenstein GR, Hanauer SB, Sandborn WJ. Management of Crohn’s disease in adults. Am J Gastroenterol. 2009;104:465–83; quiz 464, 484. - PubMed
-
- Kornbluth A, Sachar DB. Ulcerative colitis practice guidelines in adults. American College of Gastroenterology, Practice Parameters Committee. Am J Gastroenterol. 1997;92:204–211. - PubMed
-
- Bernstein CN, Wajda A, Blanchard JF. The clustering of other chronic inflammatory diseases in inflammatory bowel disease: a population-based study. Gastroenterology. 2005;129:827–836. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

