Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4-alpha involvement in liver and intestinal inflammatory networks
- PMID: 24415854
- PMCID: PMC3886012
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i1.22
Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4-alpha involvement in liver and intestinal inflammatory networks
Abstract
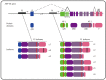
Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4-alpha (HNF4-α) is a nuclear receptor regulating metabolism, cell junctions, differentiation and proliferation in liver and intestinal epithelial cells. Mutations within the HNF4A gene are associated with human diseases such as maturity-onset diabetes of the young. Recently, HNF4A has also been described as a susceptibility gene for ulcerative colitis in genome-wide association studies. In addition, specific HNF4A genetic variants have been identified in pediatric cohorts of Crohn's disease. Results obtained from knockout mice supported that HNF4-α can protect the intestinal mucosae against inflammation. However, the exact molecular links behind HNF4-α and inflammatory bowel diseases remains elusive. In this review, we will summarize the current knowledge about the role of HNF4-α and its isoforms in inflammation. Specific nature of HNF4-α P1 and P2 classes of isoforms will be summarized. HNF4-α role as a hepatocyte mediator for cytokines relays during liver inflammation will be integrated based on documented examples of the literature. Conclusions that can be made from these earlier liver studies will serve as a basis to extrapolate correlations and divergences applicable to intestinal inflammation. Finally, potential functional roles for HNF4-α isoforms in protecting the intestinal mucosae from chronic and pathological inflammation will be presented.
Keywords: Colitis-associated cancer; Gastrointestinal tract; Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4-alpha; Inflammation; Inflammatory bowel diseases; Intestinal epithelium barrier.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Developmental and tissue-specific regulation of hepatocyte nuclear factor 4-alpha (HNF4-alpha) isoforms in rodents.Gene Expr. 2010;14(6):337-44. doi: 10.3727/105221610x12717040569901. Gene Expr. 2010. PMID: 20635575 Free PMC article.
-
Chromatin profiling reveals regulatory network shifts and a protective role for hepatocyte nuclear factor 4α during colitis.Mol Cell Biol. 2014 Sep;34(17):3291-304. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00349-14. Epub 2014 Jun 30. Mol Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 24980432 Free PMC article.
-
Immunohistochemical analysis of HNF4A and β-catenin expression to predict low-grade dysplasia in the colitis-neoplastic sequence.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2021 Jan 12;53(1):94-101. doi: 10.1093/abbs/gmaa147. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2021. PMID: 33300557
-
Development, validation and implementation of an in vitro model for the study of metabolic and immune function in normal and inflamed human colonic epithelium.Dan Med J. 2015 Jan;62(1):B4973. Dan Med J. 2015. PMID: 25557335 Review.
-
Role of hepatocyte nuclear factor 4-alpha in gastrointestinal and liver diseases.World J Gastroenterol. 2019 Aug 14;25(30):4074-4091. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i30.4074. World J Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 31435165 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
HNF4A Regulates the Proliferation and Tumor Formation of Cervical Cancer Cells through the Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 Jan 28;2022:8168988. doi: 10.1155/2022/8168988. eCollection 2022. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022. PMID: 35132353 Free PMC article.
-
Enterocyte fatty acid-binding proteins (FABPs): different functions of liver and intestinal FABPs in the intestine.Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2015 Feb;93:9-16. doi: 10.1016/j.plefa.2014.10.001. Epub 2014 Oct 14. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2015. PMID: 25458898 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A network biology workflow to study transcriptomics data of the diabetic liver.BMC Genomics. 2014 Nov 15;15(1):971. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-971. BMC Genomics. 2014. PMID: 25399255 Free PMC article.
-
Immunogenomics reveal molecular circuits of diclofenac induced liver injury in mice.Oncotarget. 2016 Mar 22;7(12):14983-5017. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.7698. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26934552 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence of widespread, independent sequence signature for transcription factor cobinding.Genome Res. 2021 Feb;31(2):265-278. doi: 10.1101/gr.267310.120. Epub 2020 Dec 10. Genome Res. 2021. PMID: 33303494 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kritis AA, Argyrokastritis A, Moschonas NK, Power S, Katrakili N, Zannis VI, Cereghini S, Talianidis I. Isolation and characterization of a third isoform of human hepatocyte nuclear factor 4. Gene. 1996;173:275–280. - PubMed
-
- Thomas H, Jaschkowitz K, Bulman M, Frayling TM, Mitchell SM, Roosen S, Lingott-Frieg A, Tack CJ, Ellard S, Ryffel GU, et al. A distant upstream promoter of the HNF-4alpha gene connects the transcription factors involved in maturity-onset diabetes of the young. Hum Mol Genet. 2001;10:2089–2097. - PubMed
-
- Furuta H, Iwasaki N, Oda N, Hinokio Y, Horikawa Y, Yamagata K, Yano N, Sugahiro J, Ogata M, Ohgawara H, et al. Organization and partial sequence of the hepatocyte nuclear factor-4 alpha/MODY1 gene and identification of a missense mutation, R127W, in a Japanese family with MODY. Diabetes. 1997;46:1652–1657. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

