Targeted cytotoxic therapy kills persisting HIV infected cells during ART
- PMID: 24415939
- PMCID: PMC3887103
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003872
Targeted cytotoxic therapy kills persisting HIV infected cells during ART
Abstract
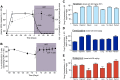
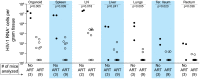
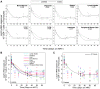
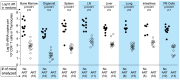
Antiretroviral therapy (ART) can reduce HIV levels in plasma to undetectable levels, but rather little is known about the effects of ART outside of the peripheral blood regarding persistent virus production in tissue reservoirs. Understanding the dynamics of ART-induced reductions in viral RNA (vRNA) levels throughout the body is important for the development of strategies to eradicate infectious HIV from patients. Essential to a successful eradication therapy is a component capable of killing persisting HIV infected cells during ART. Therefore, we determined the in vivo efficacy of a targeted cytotoxic therapy to kill infected cells that persist despite long-term ART. For this purpose, we first characterized the impact of ART on HIV RNA levels in multiple organs of bone marrow-liver-thymus (BLT) humanized mice and found that antiretroviral drug penetration and activity was sufficient to reduce, but not eliminate, HIV production in each tissue tested. For targeted cytotoxic killing of these persistent vRNA(+) cells, we treated BLT mice undergoing ART with an HIV-specific immunotoxin. We found that compared to ART alone, this agent profoundly depleted productively infected cells systemically. These results offer proof-of-concept that targeted cytotoxic therapies can be effective components of HIV eradication strategies.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Berger and Dr. Pastan report that they are co-inventors on several immunotoxin issued patents and patent applications. This does not alter our adherence to all PLOS policies on sharing data and materials. All other authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
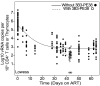
References
-
- Nakagawa F, May M, Phillips A (2013) Life expectancy living with HIV: recent estimates and future implications. Curr Opin Infect Dis 26: 17–25. - PubMed
-
- Richman DD, Margolis DM, Delaney M, Greene WC, Hazuda D, et al. (2009) The challenge of finding a cure for HIV infection. Science 323: 1304–1307. - PubMed
-
- Deeks SG (2012) HIV: Shock and kill. Nature 487: 439–440. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

