p53 and TAp63 promote keratinocyte proliferation and differentiation in breeding tubercles of the zebrafish
- PMID: 24415949
- PMCID: PMC3886889
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004048
p53 and TAp63 promote keratinocyte proliferation and differentiation in breeding tubercles of the zebrafish
Abstract
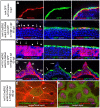
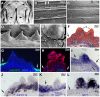
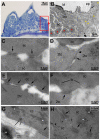
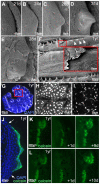
p63 is a multi-isoform member of the p53 family of transcription factors. There is compelling genetic evidence that ΔNp63 isoforms are needed for keratinocyte proliferation and stemness in the developing vertebrate epidermis. However, the role of TAp63 isoforms is not fully understood, and TAp63 knockout mice display normal epidermal development. Here, we show that zebrafish mutants specifically lacking TAp63 isoforms, or p53, display compromised development of breeding tubercles, epidermal appendages which according to our analyses display more advanced stratification and keratinization than regular epidermis, including continuous desquamation and renewal of superficial cells by derivatives of basal keratinocytes. Defects are further enhanced in TAp63/p53 double mutants, pointing to partially redundant roles of the two related factors. Molecular analyses, treatments with chemical inhibitors and epistasis studies further reveal the existence of a linear TAp63/p53->Notch->caspase 3 pathway required both for enhanced proliferation of keratinocytes at the base of the tubercles and their subsequent differentiation in upper layers. Together, these studies identify the zebrafish breeding tubercles as specific epidermal structures sharing crucial features with the cornified mammalian epidermis. In addition, they unravel essential roles of TAp63 and p53 to promote both keratinocyte proliferation and their terminal differentiation by promoting Notch signalling and caspase 3 activity, ensuring formation and proper homeostasis of this self-renewing stratified epithelium.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
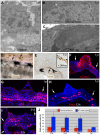

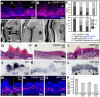
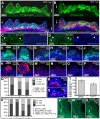
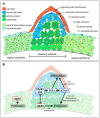
References
-
- Nakamura H, Yasuda M (1979) An electron microscopic study of periderm cell development in mouse limb buds. Anat Embryol (Berl) 157: 121–132. - PubMed
-
- Holbrook KA, Odland GF (1975) The fine structure of developing human epidermis: light, scanning, and transmission electron microscopy of the periderm. J Invest Dermatol 65: 16–38. - PubMed
-
- Byrne C, Tainsky M, Fuchs E (1994) Programming gene expression in developing epidermis. Development 120: 2369–2383. - PubMed
-
- Hardman MJ, Moore L, Ferguson MW, Byrne C (1999) Barrier formation in the human fetus is patterned. J Invest Dermatol 113: 1106–1113. - PubMed
-
- Koster MI, Roop DR (2004) The role of p63 in development and differentiation of the epidermis. J Dermatol Sci 34: 3–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

