Mean-field models for heterogeneous networks of two-dimensional integrate and fire neurons
- PMID: 24416013
- PMCID: PMC3873638
- DOI: 10.3389/fncom.2013.00184
Mean-field models for heterogeneous networks of two-dimensional integrate and fire neurons
Abstract
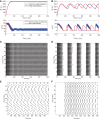
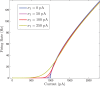
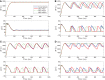
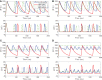
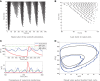
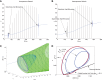
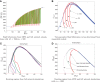
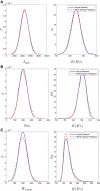
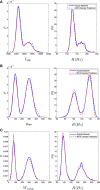
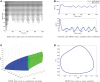
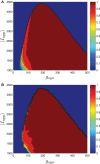
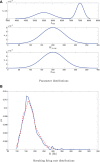
We analytically derive mean-field models for all-to-all coupled networks of heterogeneous, adapting, two-dimensional integrate and fire neurons. The class of models we consider includes the Izhikevich, adaptive exponential and quartic integrate and fire models. The heterogeneity in the parameters leads to different moment closure assumptions that can be made in the derivation of the mean-field model from the population density equation for the large network. Three different moment closure assumptions lead to three different mean-field systems. These systems can be used for distinct purposes such as bifurcation analysis of the large networks, prediction of steady state firing rate distributions, parameter estimation for actual neurons and faster exploration of the parameter space. We use the mean-field systems to analyze adaptation induced bursting under realistic sources of heterogeneity in multiple parameters. Our analysis demonstrates that the presence of heterogeneity causes the Hopf bifurcation associated with the emergence of bursting to change from sub-critical to super-critical. This is confirmed with numerical simulations of the full network for biologically reasonable parameter values. This change decreases the plausibility of adaptation being the cause of bursting in hippocampal area CA3, an area with a sizable population of heavily coupled, strongly adapting neurons.
Keywords: bifurcation analysis; bursting; hippocampus; integrate-and-fire neuron; mean-field model.
Figures
References
-
- Abbott L. F., van Vreeswijk C. (1993). Asynchronous states in networks of pulse-coupled oscillators. Learn Mem. 48, 1483–1490 - PubMed
-
- Andersen P., Morris R., Amaral D., Bliss T., O'Keefe J. (eds.). (2006). The Hippocampus Book. Oxford: Oxford University Press
-
- Bressloff P. C. (2012). Spatiotemporal dynamics of continuum neural fields. J. Phys. A. Math. Theor. 45:033001 10.1088/1751-8113/45/3/033001 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

