Recent Advances in Fiber Lasers for Nonlinear Microscopy
- PMID: 24416074
- PMCID: PMC3887125
- DOI: 10.1038/nphoton.2013.284
Recent Advances in Fiber Lasers for Nonlinear Microscopy
Abstract
Nonlinear microscopy techniques developed over the past two decades have provided dramatic new capabilities for biological imaging. The initial demonstrations of nonlinear microscopies coincided with the development of solid-state femtosecond lasers, which continue to dominate applications of nonlinear microscopy. Fiber lasers offer attractive features for biological and biomedical imaging, and recent advances are leading to high-performance sources with the potential for robust, inexpensive, integrated instruments. This article discusses recent advances, and identifies challenges and opportunities for fiber lasers in nonlinear bioimaging.
Figures
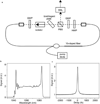

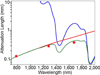
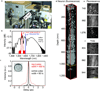

References
-
- Denk W, Strickler JH, Webb WW. Two-photon laser scanning fluorescence microscopy. Science. 1990;248:73–76. - PubMed
-
- Yuste R, Denk W. Dendritic spines as basic function units of neuronal integration. Nature. 1995;375:682–684. - PubMed
-
- Williams RM, Piston DW, Webb WW. Two-photon molecular excitation provides intrinsic 3-dimensional resolution for laser-based microscopy and microphotochemistry. FASEB J. 1994;8:804–813. - PubMed
-
- Denk W, Piston DW, Webb WW. Two-photon molecular excitation in laser scanning microscopy. In: Pawley J, editor. The Handbook of Confocal Microscopy. New York: Plenum; 1995. pp. 445–458.
-
- Helmchen F, Denk W. Deep tissue two-photon microscopy. Nat. Methods. 2005;2:932–940. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
