Clinical outcomes for gastric cancer following adjuvant chemoradiation utilizing intensity modulated versus three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy
- PMID: 24416146
- PMCID: PMC3886968
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0082642
Clinical outcomes for gastric cancer following adjuvant chemoradiation utilizing intensity modulated versus three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy
Abstract
Purpose/objectives: To determine if intensity modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) in the post-operative setting for gastric cancer was associated with reduced toxicity compared to 3D conformal radiation therapy (3DCRT).
Materials/methods: This retrospective study includes 24 patients with stage IB-IIIB gastric cancer consecutively treated from 2001-2010. All underwent surgery followed by adjuvant chemoradiation. Concurrent chemotherapy consisted of 5-FU/leucovorin (n = 21), epirubicin/cisplatin/5FU (n = 1), or none (n = 2). IMRT was utilized in 12 patients and 3DCRT in 12 patients. For both groups, the target volume included the tumor bed, anastomosis, gastric stump, and regional lymphatics.
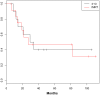
Results: Median follow-up for the entire cohort was 19 months (range 0.4-8.5 years), and 49 months (0.5-8.5 years) in surviving patients. The 3DCRT group received a median dose of 45 Gy, and the IMRT group received a median dose of 50.4 Gy (p = 0.0004). For the entire cohort, 3-year overall survival (OS) was 40% and 3-year disease free survival (DFS) was 41%. OS and DFS did not differ significantly between the groups. Acute toxicity was similar. Between 3DCRT and IMRT groups, during radiotherapy, median weight lost (3.2 vs. 3.3 kg, respectively; p = 0.47) and median percent weight loss were similar (5.0% vs. 4.3%, respectively; p = 0.43). Acute grade 2 toxicity was experienced by 8 patients receiving 3DCRT and 11 receiving IMRT (p = 0.32); acute grade 3 toxicity occurred in 1 patient receiving 3DCRT and none receiving IMRT (p = 1.0). No patients in either cohort experienced late grade 3 toxicity, including renal or gastrointestinal toxicity. At last follow up, the median increase in creatinine was 0.1 mg/dL in the IMRT group and 0.1 mg/dL in the 3DCRT group (p = 0.78).
Conclusion: This study demonstrates that adjuvant chemoradiation for gastric cancer with IMRT to 50.4 Gy was well-tolerated and compared similarly in toxicity with 3DCRT to 45 Gy.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Intensity modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) is not superior to three-dimensional conformal radiation (3DCRT) for adjuvant gastric radiation: A matched pair analysis.J Cancer Res Ther. 2015 Jul-Sep;11(3):623-9. doi: 10.4103/0973-1482.150438. J Cancer Res Ther. 2015. PMID: 26458592
-
Comparison of intensity-modulated radiotherapy and 3-dimensional conformal radiotherapy as adjuvant therapy for gastric cancer.Cancer. 2010 Aug 15;116(16):3943-52. doi: 10.1002/cncr.25246. Cancer. 2010. PMID: 20564136
-
Combined adjuvant radiochemotherapy with IMRT/XELOX improves outcome with low renal toxicity in gastric cancer.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2009 Nov 15;75(4):1187-95. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2008.12.036. Epub 2009 May 4. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2009. PMID: 19409725
-
Acute toxicity with intensity modulated radiotherapy versus 3-dimensional conformal radiotherapy during preoperative chemoradiation for locally advanced rectal cancer.Radiother Oncol. 2016 Nov;121(2):252-257. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2016.09.010. Epub 2016 Oct 14. Radiother Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27751605 Review.
-
Evolution of radiation techniques in the treatment of mediastinal lymphoma: from 3D conformal radiotherapy (3DCRT) to intensity-modulated RT (IMRT) using helical tomotherapy (HT): a single-centre experience and review of the literature.Br J Radiol. 2016;89(1059):20150409. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20150409. Epub 2016 Jan 8. Br J Radiol. 2016. PMID: 26744079 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Risk factors and patterns of lymph node involvement in primary gastric large B-cell lymphoma: implications for target definition.Onco Targets Ther. 2016 Jul 29;9:4757-62. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S110575. eCollection 2016. Onco Targets Ther. 2016. PMID: 27536138 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of intensity-modulated radiation therapy versus three-dimensional conformal radiation treatment for patients with gastric cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Radiat Oncol. 2019 May 22;14(1):84. doi: 10.1186/s13014-019-1294-0. Radiat Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31118042 Free PMC article.
-
Optimal Timing to Surgery After Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy for Locally Advanced Gastric Cancer.Front Oncol. 2020 Dec 17;10:613988. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.613988. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33392098 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of radiosensitive patients with gastric cancer by developing gene signature.Int J Oncol. 2017 Oct;51(4):1067-1076. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2017.4107. Epub 2017 Aug 30. Int J Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28902346 Free PMC article.
-
Dosimetric comparison of intensity modulated and volumetric arc radiation therapy for gastric cancer.Oncol Lett. 2014 Oct;8(4):1427-1434. doi: 10.3892/ol.2014.2363. Epub 2014 Jul 18. Oncol Lett. 2014. PMID: 25202345 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, et al. (2011) Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 61: 69–90. - PubMed
-
- Siegel R, Ward E, Brawley O, Jemal A (2011) Cancer statistics, 2011: the impact of eliminating socioeconomic and racial disparities on premature cancer deaths. CA Cancer J Clin 61: 212–236. - PubMed
-
- Macdonald JS, Smalley SR, Benedetti J, Hundahl SA, Estes NC, et al. (2001) Chemoradiotherapy after surgery compared with surgery alone for adenocarcinoma of the stomach or gastroesophageal junction. N Engl J Med 345: 725–730. - PubMed
-
- Jansen EP, Saunders MP, Boot H, Oppedijk V, Dubbelman R, et al. (2007) Prospective study on late renal toxicity following postoperative chemoradiotherapy in gastric cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 67: 781–785. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

