High serum miR-19a levels are associated with inflammatory breast cancer and are predictive of favorable clinical outcome in patients with metastatic HER2+ inflammatory breast cancer
- PMID: 24416156
- PMCID: PMC3885405
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0083113
High serum miR-19a levels are associated with inflammatory breast cancer and are predictive of favorable clinical outcome in patients with metastatic HER2+ inflammatory breast cancer
Abstract
Introduction: Altered serum microRNA (miRNA) levels may be correlated with a dysregulated expression pattern in parental tumor tissue and reflect the clinical evolution of disease. The overexpression of miR-21, miR-10b, and miR-19a is associated with the acquisition of malignant characteristics (increased tumor cell proliferation, migration, invasion, dissemination, and metastasis); thus, we determined their utility as serum biomarkers for aggressive breast cancer (HER2-overexpressed or -amplified [HER2(+)] and inflammatory breast cancer [IBC]).
Experimental design: In this prospective study, we measured miR-21, miR-10b, and miR-19a levels using quantitative reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction in the serum of 113 breast cancer patients and determined their association with clinicopathologic factors and clinical outcome. Thirty healthy donors with no history of cancer were enrolled as controls.
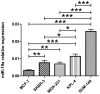
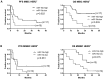
Results: Patients with non-metastatic HER2(+) breast cancer had higher serum miR-21 median levels than patients with non-metastatic HER2(-) disease (p = 0.044); whereas patients with metastatic HER2(+) breast cancer had higher serum miR-10b median levels than patients with metastatic HER2(-) disease (p = 0.0004). There were no significant differences in serum miR-19a median levels between HER2(+) and HER2(-) groups, regardless of the presence of metastases. High serum miR-19a levels were associated with IBC (p = 0.039). Patients with metastatic IBC had significantly higher serum miR-19a median levels than patients with metastatic non-IBC (p = 0.019). Finally, high serum miR-19a levels were associated with longer progression-free survival time (10.3 vs. 3.2 months; p = 0.022) and longer overall survival time (median not reached vs. 11.2 months; p = 0.003) in patients with metastatic HER2(+) IBC.
Conclusion: High levels of miR-21 and miR-10b were present in the serum of patients with non-metastatic and metastatic HER2(+) breast cancer, respectively. High levels of serum miR-19a may represent a biomarker for IBC that is predictive for favorable clinical outcome in patients with metastatic HER2(+) IBC.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Circulating Cell-free miRNA Expression and its Association with Clinicopathologic Features in Inflammatory and Non- Inflammatory Breast Cancer.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2016;17(4):1801-10. doi: 10.7314/apjcp.2016.17.4.1801. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2016. PMID: 27221856
-
Quantitative hormone receptor (HR) expression and gene expression analysis in HR+ inflammatory breast cancer (IBC) vs non-IBC.BMC Cancer. 2020 May 18;20(1):430. doi: 10.1186/s12885-020-06940-z. BMC Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32423453 Free PMC article.
-
Metastatic behavior and overall survival according to breast cancer subtypes in stage IV inflammatory breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res. 2019 Oct 17;21(1):113. doi: 10.1186/s13058-019-1201-5. Breast Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31623649 Free PMC article.
-
HER2 discordance between primary breast cancer and its paired metastasis: tumor biology or test artefact? Insights through meta-analysis.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2011 Oct;129(3):659-74. doi: 10.1007/s10549-011-1632-x. Epub 2011 Jun 23. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2011. PMID: 21698410
-
Advances from targeted therapy for non-metastatic HER2-positive inflammatory breast cancer.J Surg Oncol. 2024 Sep;130(3):366-370. doi: 10.1002/jso.27797. Epub 2024 Aug 5. J Surg Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39101322 Review.
Cited by
-
New Concepts in Cancer Biomarkers: Circulating miRNAs in Liquid Biopsies.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Apr 27;17(5):627. doi: 10.3390/ijms17050627. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27128908 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circulating miRNAs as Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarkers in Common Solid Tumors: Focus on Lung, Breast, Prostate Cancers, and Osteosarcoma.J Clin Med. 2019 Oct 11;8(10):1661. doi: 10.3390/jcm8101661. J Clin Med. 2019. PMID: 31614612 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Exosome Journey: From Biogenesis to Regulation and Function in Cancers.J Oncol. 2022 Jul 18;2022:9356807. doi: 10.1155/2022/9356807. eCollection 2022. J Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35898929 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long-Term Exercise Alters the Profiles of Circulating Micro-RNAs in the Plasma of Young Women.Front Physiol. 2020 May 8;11:372. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.00372. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32477155 Free PMC article.
-
Emergence of Circulating MicroRNAs in Breast Cancer as Diagnostic and Therapeutic Efficacy Biomarkers.Mol Diagn Ther. 2020 Apr;24(2):153-173. doi: 10.1007/s40291-020-00447-w. Mol Diagn Ther. 2020. PMID: 32067191 Review.
References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J, Ward E (2010) Cancer statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin 60: 277–300. - PubMed
-
- Cristofanilli M, Valero V, Buzdar AU, Kau SW, Broglio KR, et al. (2007) Inflammatory breast cancer (IBC) and patterns of recurrence: understanding the biology of a unique disease. Cancer 110: 1436–1444. - PubMed
-
- Mariani G, Fasolo A, De Benedictis E, Gianni L (2009) Trastuzumab as adjuvant systemic therapy for HER2-positive breast cancer. Nat Clin Pract Oncol 6: 93–104. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

