Plant-associated symbiotic Burkholderia species lack hallmark strategies required in mammalian pathogenesis
- PMID: 24416172
- PMCID: PMC3885511
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0083779
Plant-associated symbiotic Burkholderia species lack hallmark strategies required in mammalian pathogenesis
Abstract
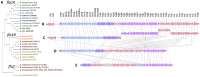
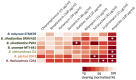
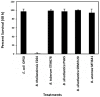
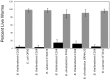
Burkholderia is a diverse and dynamic genus, containing pathogenic species as well as species that form complex interactions with plants. Pathogenic strains, such as B. pseudomallei and B. mallei, can cause serious disease in mammals, while other Burkholderia strains are opportunistic pathogens, infecting humans or animals with a compromised immune system. Although some of the opportunistic Burkholderia pathogens are known to promote plant growth and even fix nitrogen, the risk of infection to infants, the elderly, and people who are immunocompromised has not only resulted in a restriction on their use, but has also limited the application of non-pathogenic, symbiotic species, several of which nodulate legume roots or have positive effects on plant growth. However, recent phylogenetic analyses have demonstrated that Burkholderia species separate into distinct lineages, suggesting the possibility for safe use of certain symbiotic species in agricultural contexts. A number of environmental strains that promote plant growth or degrade xenobiotics are also included in the symbiotic lineage. Many of these species have the potential to enhance agriculture in areas where fertilizers are not readily available and may serve in the future as inocula for crops growing in soils impacted by climate change. Here we address the pathogenic potential of several of the symbiotic Burkholderia strains using bioinformatics and functional tests. A series of infection experiments using Caenorhabditis elegans and HeLa cells, as well as genomic characterization of pathogenic loci, show that the risk of opportunistic infection by symbiotic strains such as B. tuberum is extremely low.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Berg G, Eberl L, Hartmann A (2005) The rhizosphere as a reservoir for opportunistic human pathogenic bacteria. Environ Microbiol 7: 1673–1685. - PubMed
-
- Suárez-Moreno ZR, Caballero-Mellado J, Coutinho BG, Mendoça-Previato L, James EK, et al. (2012) Common features of environmentally and potentially beneficial plant-associated Burkholderia . Microb Ecol 63: 249–266. - PubMed
-
- Estrada-de los Santos P, Vinuesa P, Martínez-Aguilar L, Hirsch AM, Caballero-Mellado J (2013) Phylogenetic analysis of Burkholderia species by Multilocus Sequence Analysis. Curr Microbiol 67: 51–60. - PubMed
-
- Yabuuchi E, Kosako Y, Oyaizu H, Yano I, Hotta H, et al. (1992) Proposal of Burkholderia gen. nov. and transfer of seven species of the genus Pseudomonas homology group II to the new genus, with the type species Burkholderia cepacia (Palleroni and Holmes 1981) comb. nov. Microbiol Immunol 36: 1251–1275. - PubMed
-
- Yabuuchi E, Kosako Y, Yano I, Hotta H, Nishiuchi Y (1995) Transfer of two Burkholderia and an Alcaligenes species to Ralstonia gen. Nov.: Proposal of Ralstonia pickettii (Ralston, Palleroni and Doudoroff 1973) comb. Nov., Ralstonia solanacearum (Smith 1896) comb. Nov. and Ralstonia eutropha (Davis 1969) comb. Nov. Microbiol Immunol 39: 897–904. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

