Fish oil suppresses cell growth and metastatic potential by regulating PTEN and NF-κB signaling in colorectal cancer
- PMID: 24416253
- PMCID: PMC3885588
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0084627
Fish oil suppresses cell growth and metastatic potential by regulating PTEN and NF-κB signaling in colorectal cancer
Abstract
Homeostasis in eukaryotic tissues is tightly regulated by an intricate balance of the prosurvival and antisurvival signals. The tumor suppressor PTEN (phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome 10), a dual-specificity phosphatase, plays a functional role in cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. NF-κB and its downstream regulators (such as VEGF) play a central role in prevention of apoptosis, promotion of inflammation and tumor growth. Therefore, we thought to estimate the expression of PTEN, Poly-ADP-ribose polymerase (PARP), NF-κBp50, NF-κBp65 and VEGF to evaluate the effect of supplementation of fish oil on apoptotic and inflammatory signaling in colon carcinoma. Male wistar rats in Group I received purified diet while Group II and III received modified diet supplemented with FO∶CO(1∶1)&FO∶CO(2.5∶1) respectively. These were further subdivided into controls receiving ethylenediamine-tetra acetic-acid and treated groups received dimethylhydrazine-dihydrochloride (DMH)/week for 4 weeks. Animals sacrificed 48 hours after last injection constituted initiation phase and that sacrificed after 16 weeks constituted post-initiation phase. We have analysed expression of PTEN, NF-κBp50, NF-κBp65 by flowcytometer and nuclear localization of NF-κB by immunofluorescence. PARP and VEGF were assessed by immunohistochemistry. In the initiation phase, animals receiving DMH have shown increased % of apoptotic cells, PTEN, PARP, NF-κBp50, NF-κBp65 and VEGF however in post-initiation phase no significant alteration in apoptosis with decreased PTEN and increased PARP, NF-κBp50, NF-κBp65 and VEGF were observed as compared to control animals. On treatment with both ratios of fish oil in both the phases, augmentation in % of apoptotic cells, decreased PTEN, PARP, NF-κBp50, NF-κBp65 and VEGF were documented with respect to DMH treated animals with effect being more exerted with higher ration in post-initiation phase. Hence, fish oil activates apoptosis, diminishes DNA damage and inhibits inflammatory signalling in a dose and time dependent manner so as to inhibit progression of colon cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
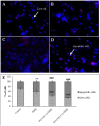


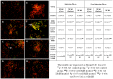


References
-
- American Cancer Society (2012). Cancer Facts and Figures 2012. Atlanta, GA: American Cancer Society. http://www.cancer.org/downloads/STT/2008CAFFfinalsecured.pdf.
-
- Barber TD, Vogelstein B, Kinzler KW, Velculescu VE (2004) Somatic mutations of EGFR in colorectal cancers and glioblastomas. N Engl J Med 351 (27) 2883. - PubMed
-
- Corvera S, Czech MP (1998) Direct targets of phosphoinositide 3-kinase products in membrane traffic and signal transduction. Trends Cell Biol 8: 442–446. - PubMed
-
- Nicholson KM, Anderson NG (2002) The protein kinase B/Akt signalling pathway in human malignancy. Cell Signal 14: 381–395. - PubMed
-
- Chang F, Lee JT, Navolanic PM, Steelman LS, Blalock WL, et al. (2003) Involvement of PI3K/Akt pathway in cell cycle progression, apoptosis, and neoplastic transformation: a target for cancer chemotherapy. Leukemia 17: 590–603. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

