Evolutionary changes in gene expression, coding sequence and copy-number at the Cyp6g1 locus contribute to resistance to multiple insecticides in Drosophila
- PMID: 24416303
- PMCID: PMC3885650
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0084879
Evolutionary changes in gene expression, coding sequence and copy-number at the Cyp6g1 locus contribute to resistance to multiple insecticides in Drosophila
Erratum in
- PLoS One. 2014;9(3):e92490
Abstract
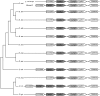
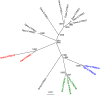
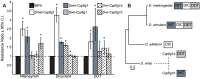
Widespread use of insecticides has led to insecticide resistance in many populations of insects. In some populations, resistance has evolved to multiple pesticides. In Drosophila melanogaster, resistance to multiple classes of insecticide is due to the overexpression of a single cytochrome P450 gene, Cyp6g1. Overexpression of Cyp6g1 appears to have evolved in parallel in Drosophila simulans, a sibling species of D. melanogaster, where it is also associated with insecticide resistance. However, it is not known whether the ability of the CYP6G1 enzyme to provide resistance to multiple insecticides evolved recently in D. melanogaster or if this function is present in all Drosophila species. Here we show that duplication of the Cyp6g1 gene occurred at least four times during the evolution of different Drosophila species, and the ability of CYP6G1 to confer resistance to multiple insecticides exists in D. melanogaster and D. simulans but not in Drosophila willistoni or Drosophila virilis. In D. virilis, which has multiple copies of Cyp6g1, one copy confers resistance to DDT and another to nitenpyram, suggesting that the divergence of protein sequence between copies subsequent to the duplication affected the activity of the enzyme. All orthologs tested conferred resistance to one or more insecticides, suggesting that CYP6G1 had the capacity to provide resistance to anthropogenic chemicals before they existed. Finally, we show that expression of Cyp6g1 in the Malpighian tubules, which contributes to DDT resistance in D. melanogaster, is specific to the D. melanogaster-D. simulans lineage. Our results suggest that a combination of gene duplication, regulatory changes and protein coding changes has taken place at the Cyp6g1 locus during evolution and this locus may play a role in providing resistance to different environmental toxins in different Drosophila species.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
High expression of Cyp6g1, a cytochrome P450 gene, does not necessarily confer DDT resistance in Drosophila melanogaster.Gene. 2007 Feb 15;388(1-2):43-53. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2006.09.019. Epub 2006 Oct 5. Gene. 2007. PMID: 17134855
-
Resistance evolution in Drosophila: the case of CYP6G1.Pest Manag Sci. 2017 Mar;73(3):493-499. doi: 10.1002/ps.4470. Epub 2016 Dec 21. Pest Manag Sci. 2017. PMID: 27787942 Review.
-
Functional and structural insights into P450-mediated resistance: The role of Cyp6g1 and Cyp6g2 in the metabolism of neonicotinoids in Drosophila melanogaster.Pestic Biochem Physiol. 2025 Aug;212:106451. doi: 10.1016/j.pestbp.2025.106451. Epub 2025 May 12. Pestic Biochem Physiol. 2025. PMID: 40500059
-
A single p450 allele associated with insecticide resistance in Drosophila.Science. 2002 Sep 27;297(5590):2253-6. doi: 10.1126/science.1074170. Science. 2002. PMID: 12351787
-
Cytochrome P450 monooxygenases and insecticide resistance in insects.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1998 Oct 29;353(1376):1701-5. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1998.0321. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1998. PMID: 10021770 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Discovery of malathion resistance QTL in Drosophila melanogaster using a bulked phenotyping approach.G3 (Bethesda). 2022 Dec 1;12(12):jkac279. doi: 10.1093/g3journal/jkac279. G3 (Bethesda). 2022. PMID: 36250804 Free PMC article.
-
Positive selection in cytochrome P450 genes is associated with gonad phenotype and mating strategy in social bees.Sci Rep. 2023 Apr 11;13(1):5921. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-32898-6. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37041178 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in Neuronal Signaling and Cell Stress Response Pathways are Associated with a Multigenic Response of Drosophila melanogaster to DDT Selection.Genome Biol Evol. 2017 Dec 1;9(12):3356-3372. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evx252. Genome Biol Evol. 2017. PMID: 29211847 Free PMC article.
-
A review of physiological resistance to insecticide stress in Nilaparvata lugens.3 Biotech. 2022 Mar;12(3):84. doi: 10.1007/s13205-022-03137-y. Epub 2022 Feb 28. 3 Biotech. 2022. PMID: 35251886 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rise of multiple insecticide resistance in Anopheles funestus in Malawi: a major concern for malaria vector control.Malar J. 2015 Sep 15;14:344. doi: 10.1186/s12936-015-0877-y. Malar J. 2015. PMID: 26370361 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Feyereisen R (2005) Insect Cytochrome P450. In: Gilbert LI, Iatrou K, Gill SS, editors. Comprehensive Molecular Insect Science. Comprehensive Molecular Insect Science. Amsterdam: Elsevier B.V., Vol. 5. pp. 1–77. Available: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B0444519246000491.
-
- Mouchès C, Pasteur N, Bergé JB, Hyrien O, Raymond M, et al. (1986) Amplification of an esterase gene is responsible for insecticide resistance in a California Culex mosquito. Science 233: 778–780. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

