Roflumilast N-oxide prevents cytokine secretion induced by cigarette smoke combined with LPS through JAK/STAT and ERK1/2 inhibition in airway epithelial cells
- PMID: 24416369
- PMCID: PMC3885699
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0085243
Roflumilast N-oxide prevents cytokine secretion induced by cigarette smoke combined with LPS through JAK/STAT and ERK1/2 inhibition in airway epithelial cells
Abstract
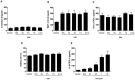
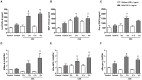
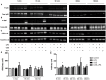
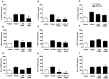
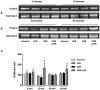
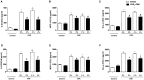
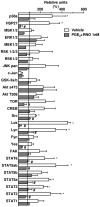
Cigarette smoke is a major cause of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Airway epithelial cells and macrophages are the first defense cells against cigarette smoke and these cells are an important source of pro-inflammatory cytokines. These cytokines play a role in progressive airflow limitation and chronic airways inflammation. Furthermore, the chronic colonization of airways by Gram-negative bacteria, contributes to the persistent airways inflammation and progression of COPD. The current study addressed the effects of cigarette smoke along with lipolysaccharide (LPS) in airway epithelial cells as a representative in vitro model of COPD exacerbations. Furthermore, we evaluated the effects of PDE4 inhibitor, the roflumilast N-oxide (RNO), in this experimental model. A549 cells were stimulated with cigarette smoke extract (CSE) alone (0.4% to 10%) or in combination with a low concentration of LPS (0.1 µg/ml) for 2 h or 24 h for measurement of chemokine protein and mRNAs and 5-120 min for protein phosphorylation. Cells were also pre-incubated with MAP kinases inhibitors and Prostaglandin E2 alone or combined with RNO, before the addition of CSE+LPS. Production of cytokines was determined by ELISA and protein phosphorylation by western blotting and phospho-kinase array. CSE did not induce production of IL-8/CXCL8 and Gro-α/CXCL1 from A549 cells, but increase production of CCL2/MCP-1. However the combination of LPS 0.1 µg/ml with CSE 2% or 4% induced an important production of these chemokines, that appears to be dependent of ERK1/2 and JAK/STAT pathways but did not require JNK and p38 pathways. Moreover, RNO associated with PGE2 reduced CSE+LPS-induced cytokine release, which can happen by occur through of ERK1/2 and JAK/STAT pathways. We report here an in vitro model that can reflect what happen in airway epithelial cells in COPD exacerbation. We also showed a new pathway where CSE+LPS can induce cytokine release from A549 cells, which is reduced by RNO.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Roflumilast N-oxide reverses corticosteroid resistance in neutrophils from patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014 Aug;134(2):314-22. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2014.02.001. Epub 2014 Mar 15. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24636089
-
Roflumilast N-oxide inhibits bronchial epithelial to mesenchymal transition induced by cigarette smoke in smokers with COPD.Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2014 Aug;28(2):138-48. doi: 10.1016/j.pupt.2014.02.001. Epub 2014 Feb 11. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2014. PMID: 24525294
-
Roflumilast N-oxide, a PDE4 inhibitor, improves cilia motility and ciliated human bronchial epithelial cells compromised by cigarette smoke in vitro.Br J Pharmacol. 2012 Aug;166(8):2243-62. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2012.01929.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22385203 Free PMC article.
-
The preclinical pharmacology of roflumilast--a selective, oral phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor in development for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2010 Aug;23(4):235-56. doi: 10.1016/j.pupt.2010.03.011. Epub 2010 Apr 7. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2010. PMID: 20381629 Review.
-
Molecular processes that drive cigarette smoke-induced epithelial cell fate of the lung.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2014 Mar;50(3):471-82. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2013-0348TR. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 24111585 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical Implication of Phosphodiesterase-4-Inhibition.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 21;23(3):1209. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031209. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35163131 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roflumilast: A Review in COPD.Drugs. 2015 Sep;75(14):1645-56. doi: 10.1007/s40265-015-0463-1. Drugs. 2015. PMID: 26338438 Review.
-
Roflumilast reduces the number of lung adenocarcinomas, inflammation, and emphysema in a smoking-induced mouse model.BMC Pulm Med. 2025 May 26;25(1):262. doi: 10.1186/s12890-025-03730-w. BMC Pulm Med. 2025. PMID: 40420271 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial Transplantation Attenuates Airway Hyperresponsiveness by Inhibition of Cholinergic Hyperactivity.Theranostics. 2016 May 24;6(8):1244-60. doi: 10.7150/thno.13804. eCollection 2016. Theranostics. 2016. PMID: 27279915 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of oral phosphatidic acid feeding with or without whey protein on muscle protein synthesis and anabolic signaling in rodent skeletal muscle.J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2015 Aug 16;12:32. doi: 10.1186/s12970-015-0094-7. eCollection 2015. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2015. PMID: 26279644 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lopez AD, Murray CC (1998) The global burden of disease, 1990–2020. Nat Med 4: 1241–1243. - PubMed
-
- Barnes PJ (2000) Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. N Engl J Med 343: 269–280. - PubMed
-
- Barnes PJ (2009) The cytokine network in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 41: 631–638. - PubMed
-
- Hogg JC, Chu F, Utokaparch S, Woods R, Elliott WM, et al. (2004) The nature of small-airway obstruction in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. N Engl J Med 350: 2645–2653. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

