SPBP is a sulforaphane induced transcriptional coactivator of NRF2 regulating expression of the autophagy receptor p62/SQSTM1
- PMID: 24416372
- PMCID: PMC3887019
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0085262
SPBP is a sulforaphane induced transcriptional coactivator of NRF2 regulating expression of the autophagy receptor p62/SQSTM1
Abstract
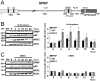
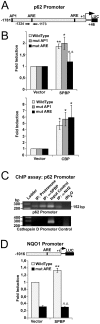
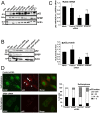
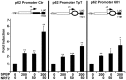
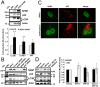
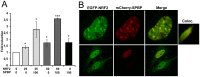
Organisms exposed to oxidative stress respond by orchestrating a stress response to prevent further damage. Intracellular levels of antioxidant agents increase, and damaged components are removed by autophagy induction. The KEAP1-NRF2 signaling pathway is the main pathway responsible for cell defense against oxidative stress and for maintaining the cellular redox balance at physiological levels. Sulforaphane, an isothiocyanate derived from cruciferous vegetables, is a potent inducer of KEAP1-NRF2 signaling and antioxidant response element driven gene expression. In this study, we show that sulforaphane enhances the expression of the transcriptional coregulator SPBP. The expression curve peaks 6-8 hours post stimulation, and parallels the sulforaphane-induced expression of NRF2 and the autophagy receptor protein p62/SQSTM1. Reporter gene assays show that SPBP stimulates the expression of p62/SQSTM1 via ARE elements in the promoter region, and siRNA mediated knock down of SPBP significantly decreases the expression of p62/SQSTM1 and the formation of p62/SQSTM1 bodies in HeLa cells. Furthermore, SPBP siRNA reduces the sulforaphane induced expression of NRF2, and the expression of the autophagy marker protein LC3B. Both these proteins contain ARE-like elements in their promoter regions. Over-expressed SPBP and NRF2 acts synergistically on the p62/SQSTM1 promoter and colocalize in nuclear speckles in HeLa cells. Collectively, these results suggest that SPBP is a coactivator of NRF2, and hence may be important for securing enhanced and sustained expression of NRF2 induced genes such as proteins involved in selective autophagy.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
p62/SQSTM1 is a target gene for transcription factor NRF2 and creates a positive feedback loop by inducing antioxidant response element-driven gene transcription.J Biol Chem. 2010 Jul 16;285(29):22576-91. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.118976. Epub 2010 May 7. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20452972 Free PMC article.
-
Arsenic inhibits autophagic flux, activating the Nrf2-Keap1 pathway in a p62-dependent manner.Mol Cell Biol. 2013 Jun;33(12):2436-46. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01748-12. Epub 2013 Apr 15. Mol Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23589329 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular cross-talk between the NRF2/KEAP1 signaling pathway, autophagy, and apoptosis.Free Radic Biol Med. 2011 May 1;50(9):1186-95. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2011.01.033. Epub 2011 Feb 2. Free Radic Biol Med. 2011. PMID: 21295136
-
p62/SQSTM1 functions as a signaling hub and an autophagy adaptor.FEBS J. 2015 Dec;282(24):4672-8. doi: 10.1111/febs.13540. Epub 2015 Oct 16. FEBS J. 2015. PMID: 26432171 Review.
-
Novel target for treating Alzheimer's Diseases: Crosstalk between the Nrf2 pathway and autophagy.Ageing Res Rev. 2021 Jan;65:101207. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2020.101207. Epub 2020 Nov 1. Ageing Res Rev. 2021. PMID: 33144123 Review.
Cited by
-
Tyrosine aminotransferase is involved in the oxidative stress response by metabolizing meta-tyrosine in Caenorhabditis elegans.J Biol Chem. 2019 Jun 14;294(24):9536-9554. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.004426. Epub 2019 May 1. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 31043480 Free PMC article.
-
Nrf2 protects mitochondrial decay by oxidative stress.FASEB J. 2016 Jan;30(1):66-80. doi: 10.1096/fj.14-268904. Epub 2015 Sep 4. FASEB J. 2016. PMID: 26340923 Free PMC article.
-
Autophagic Regulation of p62 is Critical for Cancer Therapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 May 8;19(5):1405. doi: 10.3390/ijms19051405. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29738493 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bixin protects mice against ventilation-induced lung injury in an NRF2-dependent manner.Sci Rep. 2016 Jan 5;6:18760. doi: 10.1038/srep18760. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26729554 Free PMC article.
-
Nrf2 at the heart of oxidative stress and cardiac protection.Physiol Genomics. 2018 Feb 1;50(2):77-97. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00041.2017. Epub 2017 Nov 29. Physiol Genomics. 2018. PMID: 29187515 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kensler TW, Wakabayashi N, Biswal S (2007) Cell survival responses to environmental stresses via the Keap1-Nrf2-ARE pathway. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 47: 89–116. - PubMed
-
- Hayes JD, McMahon M (2009) NRF2 and KEAP1 mutations: permanent activation of an adaptive response in cancer. Trends Biochem Sci 34: 176–188. - PubMed
-
- Uruno A, Motohashi H (2011) The Keap1-Nrf2 system as an in vivo sensor for electrophiles. Nitric Oxide 25: 153–160. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

