SPBP is a sulforaphane induced transcriptional coactivator of NRF2 regulating expression of the autophagy receptor p62/SQSTM1
- PMID: 24416372
- PMCID: PMC3887019
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0085262
SPBP is a sulforaphane induced transcriptional coactivator of NRF2 regulating expression of the autophagy receptor p62/SQSTM1
Abstract
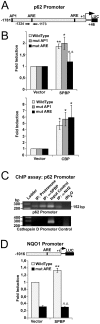
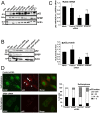
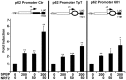
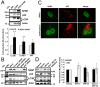
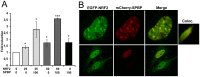
Organisms exposed to oxidative stress respond by orchestrating a stress response to prevent further damage. Intracellular levels of antioxidant agents increase, and damaged components are removed by autophagy induction. The KEAP1-NRF2 signaling pathway is the main pathway responsible for cell defense against oxidative stress and for maintaining the cellular redox balance at physiological levels. Sulforaphane, an isothiocyanate derived from cruciferous vegetables, is a potent inducer of KEAP1-NRF2 signaling and antioxidant response element driven gene expression. In this study, we show that sulforaphane enhances the expression of the transcriptional coregulator SPBP. The expression curve peaks 6-8 hours post stimulation, and parallels the sulforaphane-induced expression of NRF2 and the autophagy receptor protein p62/SQSTM1. Reporter gene assays show that SPBP stimulates the expression of p62/SQSTM1 via ARE elements in the promoter region, and siRNA mediated knock down of SPBP significantly decreases the expression of p62/SQSTM1 and the formation of p62/SQSTM1 bodies in HeLa cells. Furthermore, SPBP siRNA reduces the sulforaphane induced expression of NRF2, and the expression of the autophagy marker protein LC3B. Both these proteins contain ARE-like elements in their promoter regions. Over-expressed SPBP and NRF2 acts synergistically on the p62/SQSTM1 promoter and colocalize in nuclear speckles in HeLa cells. Collectively, these results suggest that SPBP is a coactivator of NRF2, and hence may be important for securing enhanced and sustained expression of NRF2 induced genes such as proteins involved in selective autophagy.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Kensler TW, Wakabayashi N, Biswal S (2007) Cell survival responses to environmental stresses via the Keap1-Nrf2-ARE pathway. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 47: 89–116. - PubMed
-
- Hayes JD, McMahon M (2009) NRF2 and KEAP1 mutations: permanent activation of an adaptive response in cancer. Trends Biochem Sci 34: 176–188. - PubMed
-
- Uruno A, Motohashi H (2011) The Keap1-Nrf2 system as an in vivo sensor for electrophiles. Nitric Oxide 25: 153–160. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

