Tamoxifen in breast cancer ipse dixit in uterine malignant mixed Müllerian tumor and sarcoma-A report of 8 cases and review of the literature
- PMID: 24416561
- PMCID: PMC3863172
- DOI: 10.1016/j.rpor.2013.06.005
Tamoxifen in breast cancer ipse dixit in uterine malignant mixed Müllerian tumor and sarcoma-A report of 8 cases and review of the literature
Abstract
Aim: Report the outcome of 8 patients (pts) with breast cancer (BC) treated with Tamoxifen (TAM) that developed malignant mixed Müllerian tumor (MMMT) and rare uterine sarcoma (RUS).
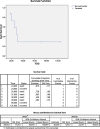
Patients and methods: Retrospective study based on data collected from the department medical records between April 1999 and September 2010 among 583 pts with endometrial cancer, 36 pts with MMMT and RUS histopathology. Among them, 8 pts underwent TAM between 4 and 10 years due to a previous diagnosis of BC; all pts were post-menopausal with regular gynecological surveillance; 6 pts (75%) with abnormal uterine bleeding. The diagnosis of 6 pts (MMMT) and 2 pts (RUS) occurred at median interval of 8 years (range 4-12) after initial BC treatment. Pts underwent surgical treatment and were staged as stage I (3pts), IIIA (3pts) and IIIC (2 pts) (FIGO 1988); followed by whole pelvis irradiation (50 Gy) and intracavitary HDR brachytherapy boost (24 Gy). Two pts underwent chemotherapy (CT). Overall and disease free survival was calculated by Kaplan Meier method.
Results: With a median follow-up of 47 months (range 17-130), 3 pts remain alive recurrence-free of BC and RUS. Four pts died with distant metastasis within the first follow-up year, without BC. One pt died from non-related cancer cause. No evidence of local recurrence was found in the whole group of pts. At two years, DFS and OS were 40% and 80%, respectively.
Conclusion: As reported in the literature, TAM administration and causal effect on MMMT and RUS in BC pts is still unknown. No reports about outcome from these specific pts were found.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Pelvic irradiation; Tamoxifen-related uterine sarcoma.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Uterine malignant mixed Müllerian tumor after adjuvant tamoxifen treatment for breast cancer.Eur J Gynaecol Oncol. 2013;34(1):94-8. Eur J Gynaecol Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23590011
-
Malignant mixed Müllerian tumors of the uterus: analysis of patterns of failure, prognostic factors, and treatment outcome.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2004 Mar 1;58(3):786-96. doi: 10.1016/S0360-3016(03)01561-X. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2004. PMID: 14967435
-
Development of uterine sarcoma after tamoxifen treatment for breast cancer: report of four cases.Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2005 Nov-Dec;15(6):1239-42. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1438.2005.00170.x. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2005. PMID: 16343223
-
Long-term tamoxifen treatment: a possible aetiological factor in the development of uterine carcinosarcoma: two case-reports and review of the literature.Anticancer Res. 2000 May-Jun;20(3B):2015-20. Anticancer Res. 2000. PMID: 10928144 Review.
-
Treatment results of high-dose-rate remote afterloading brachytherapy for cervical cancer and retrospective comparison of two regimens.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2003 Apr 1;55(5):1254-64. doi: 10.1016/s0360-3016(02)04525-x. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2003. PMID: 12654435 Review.
Cited by
-
Risk and prognostic factors for endometrial carcinoma after diagnosis of breast or Lynch-associated cancers-A population-based analysis.Cancer Med. 2018 Dec;7(12):6411-6422. doi: 10.1002/cam4.1890. Epub 2018 Nov 28. Cancer Med. 2018. PMID: 30485707 Free PMC article.
-
Uterine Malignant Mixed Müllerian Tumors Following Treatment with Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators in Patients with Breast Cancer: A Report of 13 Cases and Their Clinicopathologic Characteristics.J Pathol Transl Med. 2019 Jan;53(1):31-39. doi: 10.4132/jptm.2018.11.16. Epub 2018 Dec 18. J Pathol Transl Med. 2019. PMID: 30558398 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of Breast Cancer Patients' Knowledge and Decisional Conflict Regarding Tamoxifen Use.J Korean Med Sci. 2015 Nov;30(11):1604-10. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2015.30.11.1604. Epub 2015 Oct 16. J Korean Med Sci. 2015. PMID: 26539004 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ferlay J., Shin H.-R., Bray F., Forman D., Mathers C., Parkin D.M. Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 2010;127:2893–2917. - PubMed
-
- Fisher B., Dignam J., Wolmark N. Tamoxifen in treatment of intraductal breast cancer: National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project B-24 randomized controlled trial. Lancet. 1999;353(June (9169)):1993–2000. - PubMed
-
- Fisher B., Costantino J.P., Wickerham D.L. Tamoxifen for prevention of breast cancer: report of the National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project P-1 Study. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1998;90(September (18)):1371–1388. - PubMed
-
- Tamoxifen for early breast cancer: an overview of the randomised trials. Early Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative Group. Lancet. 1998;351(May (9114)):1451–1467. [editorial] - PubMed
-
- Zaloudek C., Norris H.J. Mesenchymal tumors of the uterus. In: Kurman R.J., editor. Blaustein's: pathology of the female genital tract. Springer-Verlag; New York: 1987. pp. 398–401.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous