Morphometric parameters of peripheral nerves in calves correlated with conduction velocity
- PMID: 24417498
- PMCID: PMC4857965
- DOI: 10.1111/jvim.12271
Morphometric parameters of peripheral nerves in calves correlated with conduction velocity
Abstract
Background: Peripheral nerve injuries are the most frequent neurologic disorder in cattle. So far, no physiologic values have been established for the motor nerve conduction velocity (mNCV) in this precocial species.
Objectives: The electrophysiologic and morphometric reference values of peripheral nerves in calves were determined. It was hypothesized that these parameters would correlate to the high degree of maturity in the first days of life in this species compared to other species.
Animals: Twenty-six healthy calves were used in this study.
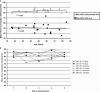
Methods: The mNCV of the radial and the sciatic/common peroneal nerve was measured in all 26 calves. Nerve biopsies from a group of 6 calves were taken to correlate the obtained electrophysiologic data with morphological parameters.
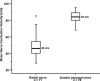
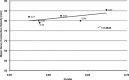
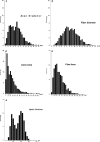
Results: The mean mNCV of the radial nerve was 48.3 ± 10.6 m/s, whereas the mean mNCV of the sciatic/peroneal nerve was with 83.8 ± 5.9 m/s significantly faster (P < .0001). The average fiber diameter was 8.40 ± 2.80 μm (range, 1.98-17.90 μm) and the average g-ratio was 0.61 ± 0.04 SD.
Conclusion and clinical importance: The established reference values for mNCV in calves correlate well with the evaluated morphometric parameters. Attributable to their comparably fast mNCV and high fiber diameters, juvenile calves appear to be much more mature individuals than other mammals. Electrophysiologic characterization of peripheral nerve injury now is feasible in this species.
Keywords: Myelination; Precocial species; g-ratio.
Copyright © 2014 by the American College of Veterinary Internal Medicine.
Figures


Similar articles
-
NT-3 attenuates functional and structural disorders in sensory nerves of galactose-fed rats.J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1998 Sep;57(9):803-13. doi: 10.1097/00005072-199809000-00001. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1998. PMID: 9737543
-
Sensory and motor maximum nerve conduction velocity in the peripheral and central nervous system of the beagle dog.Agents Actions. 1982 Oct;12(4):566-74. doi: 10.1007/BF01965943. Agents Actions. 1982. PMID: 7180741
-
Methods of clinical electrophysiologic study in pigs.Am J Vet Res. 1989 Nov;50(11):1820-2. Am J Vet Res. 1989. PMID: 2619110
-
Effects of a new aldose reductase inhibitor, (2S, 4S)-6-fluoro-2',5'-dioxospiro[chroman-4,4'-imidazolidine]-2-ca rboxamid e (SNK-860), on the slowing of motor nerve conduction velocity and metabolic abnormalities in the peripheral nerve in acute streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats.Metabolism. 1992 Oct;41(10):1081-6. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(92)90289-m. Metabolism. 1992. PMID: 1328819
-
Lower extremity sensory nerve conduction studies.Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am. 1998 Nov;9(4):853-70, vii. Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am. 1998. PMID: 9894099 Review.
Cited by
-
Use of Electrodiagnostics in the Diagnosis and Follow-Up of Brachial Plexus Syndrome in a Calf.Vet Sci. 2022 Mar 15;9(3):136. doi: 10.3390/vetsci9030136. Vet Sci. 2022. PMID: 35324865 Free PMC article.
-
Preclinical study of peripheral nerve regeneration using nerve guidance conduits based on polyhydroxyalkanaotes.Bioeng Transl Med. 2021 May 21;6(3):e10223. doi: 10.1002/btm2.10223. eCollection 2021 Sep. Bioeng Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 34589600 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the effect of pitavastatin on motor deficit and functional recovery in sciatic nerve injury: A CatWalk study.Turk J Phys Med Rehabil. 2023 Jun 11;69(3):334-343. doi: 10.5606/tftrd.2023.11002. eCollection 2023 Sep. Turk J Phys Med Rehabil. 2023. PMID: 37674804 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Steiss JE. Electrodiagnostic evaluation In: Braund KG, Vite CH, ed. Clinical Neurology in Small Animals: Localization, Diagnosis and Treatment. Ithaca NY: International Veterinary Information Service, 2003; A3232.0203, [cited 2013 Jan 12]. Available from: http://www.ivis.org/advances/Vite/steiss1/chapter_frm.asp?LA=1.
-
- Hursh JB. Conduction velocity and diameter of nerve fibers. Am J Physiol 1939;127:131–139.
-
- Hursh JB. The properties of growing nerve fibers. Am J Physiol 1939;127:140–153.
-
- Swallow JS, Griffiths IR. Age related changes in the motor nerve conduction velocity in dogs. Res Vet Sci 1977;23:29–32. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

