Morphometric parameters of peripheral nerves in calves correlated with conduction velocity
- PMID: 24417498
- PMCID: PMC4857965
- DOI: 10.1111/jvim.12271
Morphometric parameters of peripheral nerves in calves correlated with conduction velocity
Abstract
Background: Peripheral nerve injuries are the most frequent neurologic disorder in cattle. So far, no physiologic values have been established for the motor nerve conduction velocity (mNCV) in this precocial species.
Objectives: The electrophysiologic and morphometric reference values of peripheral nerves in calves were determined. It was hypothesized that these parameters would correlate to the high degree of maturity in the first days of life in this species compared to other species.
Animals: Twenty-six healthy calves were used in this study.
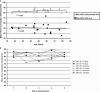
Methods: The mNCV of the radial and the sciatic/common peroneal nerve was measured in all 26 calves. Nerve biopsies from a group of 6 calves were taken to correlate the obtained electrophysiologic data with morphological parameters.
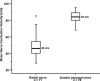
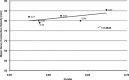
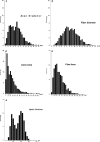
Results: The mean mNCV of the radial nerve was 48.3 ± 10.6 m/s, whereas the mean mNCV of the sciatic/peroneal nerve was with 83.8 ± 5.9 m/s significantly faster (P < .0001). The average fiber diameter was 8.40 ± 2.80 μm (range, 1.98-17.90 μm) and the average g-ratio was 0.61 ± 0.04 SD.
Conclusion and clinical importance: The established reference values for mNCV in calves correlate well with the evaluated morphometric parameters. Attributable to their comparably fast mNCV and high fiber diameters, juvenile calves appear to be much more mature individuals than other mammals. Electrophysiologic characterization of peripheral nerve injury now is feasible in this species.
Keywords: Myelination; Precocial species; g-ratio.
Copyright © 2014 by the American College of Veterinary Internal Medicine.
Figures


References
-
- Steiss JE. Electrodiagnostic evaluation In: Braund KG, Vite CH, ed. Clinical Neurology in Small Animals: Localization, Diagnosis and Treatment. Ithaca NY: International Veterinary Information Service, 2003; A3232.0203, [cited 2013 Jan 12]. Available from: http://www.ivis.org/advances/Vite/steiss1/chapter_frm.asp?LA=1.
-
- Hursh JB. Conduction velocity and diameter of nerve fibers. Am J Physiol 1939;127:131–139.
-
- Hursh JB. The properties of growing nerve fibers. Am J Physiol 1939;127:140–153.
-
- Swallow JS, Griffiths IR. Age related changes in the motor nerve conduction velocity in dogs. Res Vet Sci 1977;23:29–32. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

