Gender and incidence of dementia in the Framingham Heart Study from mid-adult life
- PMID: 24418058
- PMCID: PMC4092061
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jalz.2013.10.005
Gender and incidence of dementia in the Framingham Heart Study from mid-adult life
Abstract
Background: Gender-specific risks for dementia and Alzheimer's disease (AD) starting in midlife remain largely unknown.
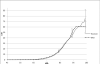
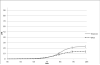
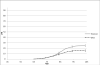
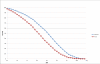
Methods: Prospectively ascertained dementia/AD and cause-specific mortality in Framingham Heart Study (FHS) participants was used to generate 10- to 50-year risk estimates of dementia/AD on the basis of the Kaplan-Meier method (cumulative incidence) or accounting for competing risk of death (lifetime risk [LTR]).
Results: Overall, 777 cases of incident dementia (601 AD) occurred in 7901 participants (4333 women) over 136,266 person-years. Whereas cumulative incidences were similar in women and men, LTRs were higher in women older than 85 years of age. LTR of dementia/AD at age 45 was 1 in 5 in women and 1 in 10 in men. Cardiovascular mortality was higher in men with rate ratios decreasing from approximately 6 at 45 to 54 years of age to less than 2 after age 65.
Conclusion: Selective survival of men with a healthier cardiovascular risk profile and hence lower propensity to dementia might partly explain the higher LTR of dementia/AD in women.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; Cardiovascular risk profile; Cohort/population-based cohort; Gender; Incidence of dementia; Mortality; Prevention; Selective survival.
Copyright © 2015 The Alzheimer's Association. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Kivipelto M, Ngandu T, Laatikainen T, Winblad B, Soininen H, Tuomilehto J. Risk score for the prediction of dementia risk in 20 years among middle aged people: a longitudinal, population-based study. Lancet Neurol. 2006;5:735–41. - PubMed
-
- Lambert JC, Heath S, Even G, Campion D, Sleegers K, Hiltunen M, et al. Genome-wide association study identifies variants at CLU and CR1 associated with Alzheimer's disease. Nat Genet. 2009;41:1094–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- N01-HC-25195/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS017950/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG016495/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL096917/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC025195/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- AG033193/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG08122/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG008122/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- HL93029/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- AG031287/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG031287/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL093029/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- NS17950/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U01HL096917/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC025195/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG033193/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG16495/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG010129/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

