MUC1: a novel metabolic master regulator
- PMID: 24418575
- PMCID: PMC4045475
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2014.01.001
MUC1: a novel metabolic master regulator
Abstract
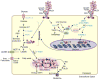
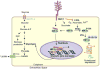
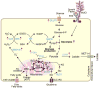
MUC1, a type I transmembrane protein, is significantly overexpressed and aberrantly glycosylated in tumors of epithelial origin. By virtue of its aberrant signaling due to loss of apical-basal polarity in cancer, MUC1 regulates the metabolite flux at multiple levels. Serving as a transcriptional co-activator, MUC1 directly regulates expression of metabolic genes. By regulating receptor tyrosine kinase signaling, MUC1 facilitates production of biosynthetic intermediates required for cell growth. Also, via direct interactions, MUC1 modulates the activity/stability of enzymes and transcription factors that directly regulate metabolic functions. Additionally, by modulation of autophagy, levels of reactive oxygen species, and metabolite flux, MUC1 facilitates cancer cell survival under hypoxic and nutrient-deprived conditions. This article provides a comprehensive review of recent literature on novel metabolic functions of MUC1.
Keywords: Cancer metabolism; Glycolysis; MUC1; Nutrient stress and carbon flux.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Lan MS, Batra SK, Qi WN, Metzgar RS, Hollingsworth MA. Cloning and sequencing of a human pancreatic tumor mucin cDNA. The Journal of biological chemistry. 1990;265:15294–15299. - PubMed
-
- Gendler S, Taylor-Papadimitriou J, Duhig T, Rothbard J, Burchell J. A highly immunogenic region of a human polymorphic epithelial mucin expressed by carcinomas is made up of tandem repeats. The Journal of biological chemistry. 1988;263:12820–12823. - PubMed
-
- Spicer AP, Parry G, Patton S, Gendler SJ. Molecular cloning and analysis of the mouse homologue of the tumor-associated mucin, MUC1, reveals conservation of potential O-glycosylation sites, transmembrane, and cytoplasmic domains and a loss of minisatellite-like polymorphism. The Journal of biological chemistry. 1991;266:15099–15109. - PubMed
-
- Singh PK, Hollingsworth MA. Cell surface-associated mucins in signal transduction. Trends Cell Biol. 2006;16:467–476. - PubMed
-
- Tanida S, Akita K, Ishida A, Mori Y, Toda M, Inoue M, Ohta M, Yashiro M, Sawada T, Hirakawa K, Nakada H. Binding of the sialic acid binding lectin, Siglec-9, to the membrane mucin, MUC1, induces recruitment of beta-catenin and subsequent cell growth. The Journal of biological chemistry. 2013 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

