Purification, crystallization and preliminary X-ray analysis of the inverse F-BAR domain of the human srGAP2 protein
- PMID: 24419634
- PMCID: PMC3943097
- DOI: 10.1107/S2053230X13033712
Purification, crystallization and preliminary X-ray analysis of the inverse F-BAR domain of the human srGAP2 protein
Abstract
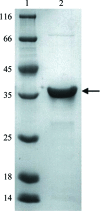
Bin-Amphiphysin-Rvs (BAR) domain proteins play essential roles in diverse cellular processes by inducing membrane invaginations or membrane protrusions. Among the BAR superfamily, the `classical' BAR and Fes/CIP4 homology BAR (F-BAR) subfamilies of proteins usually promote membrane invaginations, whereas the inverse BAR (I-BAR) subfamily generally incur membrane protrusions. Despite possessing an N-terminal F-BAR domain, the srGAP2 protein regulates neurite outgrowth and neuronal migration by causing membrane protrusions reminiscent of the activity of I-BAR domain proteins. In this study, the inverse F-BAR (IF-BAR) domain of human srGAP2 was overexpressed, purified and crystallized. The crystals of the srGAP2 IF-BAR domain protein diffracted to 3.50 Å resolution and belonged to space group P2(1). These results will facilitate further structural determination of the srGAP2 IF-BAR domain and the ultimate elucidation of its peculiar behaviour of inducing membrane protrusions rather than membrane invaginations.
Keywords: human srGAP2; inverse F-BAR domain.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Molecular symmetry-constrained systematic search approach to structure solution of the coiled-coil SRGAP2 F-BARx domain.Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol. 2016 Dec 1;72(Pt 12):1241-1253. doi: 10.1107/S2059798316016697. Epub 2016 Nov 29. Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol. 2016. PMID: 27917825
-
The inverse F-BAR domain protein srGAP2 acts through srGAP3 to modulate neuronal differentiation and neurite outgrowth of mouse neuroblastoma cells.PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e57865. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0057865. Epub 2013 Mar 7. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23505444 Free PMC article.
-
The F-BAR domain of srGAP2 induces membrane protrusions required for neuronal migration and morphogenesis.Cell. 2009 Sep 4;138(5):990-1004. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.06.047. Cell. 2009. PMID: 19737524 Free PMC article.
-
F-BAR family proteins, emerging regulators for cell membrane dynamic changes-from structure to human diseases.J Hematol Oncol. 2015 May 9;8:47. doi: 10.1186/s13045-015-0144-2. J Hematol Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25956236 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Subcellular membrane curvature mediated by the BAR domain superfamily proteins.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2010 Jun;21(4):340-9. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2009.12.002. Epub 2009 Dec 4. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2010. PMID: 19963073 Review.
Cited by
-
Mind the (sr)GAP - roles of Slit-Robo GAPs in neurons, brains and beyond.J Cell Sci. 2017 Dec 1;130(23):3965-3974. doi: 10.1242/jcs.207456. Epub 2017 Nov 2. J Cell Sci. 2017. PMID: 29097383 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

