Development of a novel enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay to detect anti-IgG against swine hepatitis E virus
- PMID: 24421718
- PMCID: PMC3885741
- DOI: 10.4142/jvs.2013.14.4.467
Development of a novel enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay to detect anti-IgG against swine hepatitis E virus
Abstract
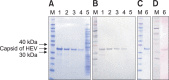
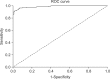
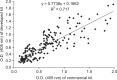
Swine hepatitis E virus (HEV) is widespread throughout pigs in both developing and industrialized countries. This virus is an important zoonotic agent and a public concern worldwide. Infected pigs are asymptomatic, so diagnosing swine HEV relies on detection of the virus or antibodies against the virus. However, several obstacles need to be overcome for effective and practical serological diagnosis. In this study, we developed an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) that used a purified recombinant capsid protein of swine HEV. The potential clinical use of this assay was evaluated by comparing it with a commercial kit (Genelabs Technologies, Diagnostics, Singapore). Results of the ELISA were highly correlated with those of the commercial kit with a sensitivity of 97% and specificity of 95%. ROC (receiving operator characteristic) analysis of the ELISA data produced a value of 0.987 (95% CI, 0.977~0.998, p < 0.01). The cut-off value for the ELISA was also determined using negative pig sera. In summary, the HEV-specific ELISA developed in the present study appears to be both practical and economical.
Keywords: ELISA; diagnosis; swine hepatitis E virus.
Figures

References
-
- Aggarwal R. Diagnosis of hepatitis E. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013;10:24–33. - PubMed
-
- Arankalle VA, Tsarev SA, Chadha MS, Alling DW, Emerson SU, Banerjee K, Purcell RH. Age-specific prevalence of antibodies to hepatitis A and E viruses in Pune, India, 1982 and 1992. J Infect Dis. 1995;171:447–450. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

