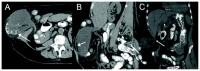
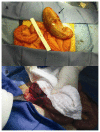
Gallbladder torsion resulting in gangrenous cholecystitis within a parastomal hernia: findings on unenhanced CT
- PMID: 24421934
- PMCID: PMC3888327
- DOI: 10.3941/jrcr.v7i12.1518
Gallbladder torsion resulting in gangrenous cholecystitis within a parastomal hernia: findings on unenhanced CT
Abstract
Gallbladder torsion is a rare cause of acute gangrenous cholecystitis; its occurrence within an abdominal hernia has not been previously reported. We present such a case occurring within a parastomal hernia and imaged with unenhanced CT.
Keywords: acute cholecystitis; gallbladder torsion; gallbladder volvulus; gangrenous cholecystitis; parastomal hernia.
Figures
References
-
- Lemonick DM, Garvin R, Semins H. Torsion of the gallbladder: a rare cause of acute cholecystitis. J Emerg Med. 2006;30(4):397–401. - PubMed
-
- Nakao A, Matsuda T, Funabiki S, et al. Gallbladder torsion: case report and review of 245 cases reported in the Japanese literature. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 1999;6(4):418–421. - PubMed
-
- McHenry CR, Byrne MP. Gallbladder volvulus in the elderly. An emergent surgical disease. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1986;34:137–139. - PubMed
-
- Hinoshita E, Nishizaki T, Wakasugi K, et al. Pre-operative imaging can diagnose torsion of the gallbladder: report of a case. Hepatogastroenterology. 1999;46:2212–2215. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical