IGF-1 regulation of key signaling pathways in bone
- PMID: 24422135
- PMCID: PMC3818534
- DOI: 10.1038/bonekey.2013.171
IGF-1 regulation of key signaling pathways in bone
Abstract
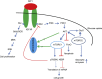
Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) is an unique peptide that functions in an endocrine/paracrine and autocrine manner in most tissues. Although it was postulated initially that liver-derived IGF-1 was the major source of IGF-1 (that is, the somatomedin hypothesis), it is also produced in a wide variety of tissues and can function in numerous ways as both a proliferative and differentiative factor. One such tissue is bone and all cell lineages in the skeleton have been shown to not only require IGF-1 for normal development and function but also to respond to IGF-1 via the IGF-1 receptor. Ligand-receptor activation leads to several distinct downstream signaling cascades, which have significant implications for cell survival, protein synthesis and energy utilization. The novel role of IGF-1 in regulating metabolic demands of the bone remodeling unit is currently under investigation. More studies are likely to shed new light on various aspects of skeletal physiology and potentially may lead to new therapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Type I insulin-like growth factor receptor signaling in skeletal muscle regeneration and hypertrophy.J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2007 Jul-Sep;7(3):208-18. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2007. PMID: 17947802 Review.
-
Cooperation of liver cells in health and disease.Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. 2001;161:III-XIII, 1-151. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-56553-3. Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11729749 Review.
-
Skeletal actions of insulin-like growth factors.Expert Rev Endocrinol Metab. 2006 Jan;1(1):47-56. doi: 10.1586/17446651.1.1.47. Expert Rev Endocrinol Metab. 2006. PMID: 30743768
-
A transgenic model to determine the physiological role of liver-derived insulin-like growth factor I.Minerva Endocrinol. 2002 Dec;27(4):299-311. Minerva Endocrinol. 2002. PMID: 12511852 Review.
-
Autocrine and Paracrine Actions of IGF-I Signaling in Skeletal Development.Bone Res. 2013 Sep 25;1(3):249-59. doi: 10.4248/BR201303003. eCollection 2013 Sep. Bone Res. 2013. PMID: 26273506 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Gut microbial-derived short-chain fatty acids and bone: a potential role in fracture healing.Eur Cell Mater. 2021 Apr 21;41:454-470. doi: 10.22203/eCM.v041a29. Eur Cell Mater. 2021. PMID: 33881768 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluating the local expression pattern of IGF-1R in tumor tissues and the circulating levels of IGF-1, IGFBP-1, and IGFBP-3 in the blood of patients with different primary bone tumors.Front Oncol. 2023 Jan 13;12:1096438. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1096438. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36713521 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Bone Metabolism.Rep Biochem Mol Biol. 2017 Apr;5(2):73-82. Rep Biochem Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28367467 Free PMC article.
-
A case-control study analyzing the association of keloids with hypertension and obesity.Int J Dermatol. 2017 Sep;56(9):e187-e189. doi: 10.1111/ijd.13618. Epub 2017 May 11. Int J Dermatol. 2017. PMID: 28497468 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Involvement of Noncoding RNAs in the Differentiation of Osteoclasts.Stem Cells Int. 2020 Aug 25;2020:4813140. doi: 10.1155/2020/4813140. eCollection 2020. Stem Cells Int. 2020. PMID: 32908541 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Efstratiadis A. Genetics of mouse growth. Int J Dev Biol 1998;42:955–976. - PubMed
-
- Hernández-Sánchez C, Blakesley V, Kalebic T, Helman L, LeRoith D. The role of the tyrosine kinase domain of the insulin-like growth factor-I receptor in intracellular signaling, cellular proliferation, and tumorigenesis. J Biol Chem 1995;270:29176–29181. - PubMed
-
- Baker J, Liu JP, Robertson EJ, Efstratiadis A. Role of insulin-like growth factors in embryonic and postnatal growth. Cell 1993;75:73–82. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
