Mumps virus infection in vaccinated patients can be detected by an increase in specific IgG antibodies to high titres: a retrospective study
- PMID: 24423404
- PMCID: PMC9151285
- DOI: 10.1017/S0950268813003427
Mumps virus infection in vaccinated patients can be detected by an increase in specific IgG antibodies to high titres: a retrospective study
Abstract
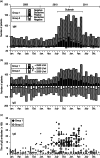
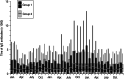
Mumps outbreaks in highly vaccinated populations with genotype G have been reported repeatedly. Detection of these outbreaks can be difficult in a setting with relatively high vaccination coverage when acute cases of mumps are routinely diagnosed by IgM serology since this marker is not reliable for diagnosis of mumps re-infection. To learn whether diagnostic tests performed in a large private laboratory may be useful to detect mumps outbreaks retrospectively, we reviewed the results of almost 7000 mumps tests. Two groups were compared: group 1 comprised of 3438 samples from patients submitted by physicians and clinicians (it was assumed that these patients visited their doctor due to acute disease). Group 2 comprised of 3398 samples submitted from company medical officers and occupational physicians. Since these patients usually attend for routine check-ups and certification of immunity to vaccine-preventable diseases, these samples comprised a control group. From July 2010 to May 2011, a mumps virus outbreak with more than 300 cases occurred in Bavaria, Southeast Germany. Our study includes samples received for serological mumps tests from January 2009 until December 2011 (36 months). The two groups were analysed with regard to the number of IgM-positive cases per month and the level of IgG titre. We found a marked increase for both parameters in group 1 during the time of the outbreak, while the samples submitted by the occupational medical physicians did not display significant alterations. These parameters reflect the outbreak with high accuracy, indicating that a retrospective analysis of IgG titres may be a useful tool for detection of mumps outbreaks when, as was the case in Germany, (i) a nationwide notification system has not been implemented and (ii) a highly vaccinated population is affected.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Contribution of the detection of IgA antibodies to the laboratory diagnosis of mumps in the population with a high vaccination coverage].Epidemiol Mikrobiol Imunol. 2015 Mar;64(1):16-9. Epidemiol Mikrobiol Imunol. 2015. PMID: 25872991 Czech.
-
A protracted mumps outbreak in Western Australia despite high vaccine coverage: a population-based surveillance study.Lancet Infect Dis. 2019 Feb;19(2):177-184. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(18)30498-5. Epub 2018 Dec 14. Lancet Infect Dis. 2019. PMID: 30558994
-
[The benefit from mumps virus IgG antibody avidity testing in the population with high vaccine coverage in the context of other serological methods for laboratory diagnosis of mumps and the current epidemiological].Epidemiol Mikrobiol Imunol. 2016 Winter;65(1):39-44. Epidemiol Mikrobiol Imunol. 2016. PMID: 27246643 Czech.
-
Mumps outbreak among young people in Northern Ireland.Commun Dis Public Health. 2001 Dec;4(4):311-5. Commun Dis Public Health. 2001. PMID: 12109401 Review.
-
Mumps in the Vaccination Age: Global Epidemiology and the Situation in Germany.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2018 Jul 31;15(8):1618. doi: 10.3390/ijerph15081618. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2018. PMID: 30065192 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Resurgence of mumps in Korea.Infect Chemother. 2015 Mar;47(1):1-11. doi: 10.3947/ic.2015.47.1.1. Epub 2015 Mar 30. Infect Chemother. 2015. PMID: 25844258 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pericardial Tamponade in an Adult Suffering from Acute Mumps Infection.Case Rep Med. 2016;2016:7980936. doi: 10.1155/2016/7980936. Epub 2016 Oct 12. Case Rep Med. 2016. PMID: 27818687 Free PMC article.
-
Serologic Cross-Reactivity between the Mumps Virus Vaccine Genotype A Strain and the Circulating Genotype G Strain.Viruses. 2024 Sep 8;16(9):1434. doi: 10.3390/v16091434. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 39339910 Free PMC article.
-
Mumps Virus SH Protein Inhibits NF-κB Activation by Interacting with Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor 1, Interleukin-1 Receptor 1, and Toll-Like Receptor 3 Complexes.J Virol. 2017 Aug 24;91(18):e01037-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01037-17. Print 2017 Sep 15. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 28659487 Free PMC article.
-
Mumps serum antibody levels before and after an outbreak to assess infection and immunity in vaccinated students.Open Forum Infect Dis. 2014 Nov 13;1(3):ofu101. doi: 10.1093/ofid/ofu101. eCollection 2014 Dec. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2014. PMID: 25734169 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barskey AE, et al. Mumps outbreak in Orthodox Jewish communities in the United States. New England Journal Medicine 2012; 367: 1704–1713. - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Mumps epidemic – United Kingdom, 2004–2005. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Reports 2006; 55: 173–175. - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Brief report: update: mumps activity – United States, January 1–October 7, 2006. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Reports 2006; 55: 1152–1153. - PubMed
-
- Fanoy EB, et al. Transmission of mumps virus from mumps-vaccinated individuals to close contacts. Vaccine 2011; 29: 9551–9556. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

