Modulation of keratinocyte expression of antioxidants by 4-hydroxynonenal, a lipid peroxidation end product
- PMID: 24423726
- PMCID: PMC4167054
- DOI: 10.1016/j.taap.2014.01.001
Modulation of keratinocyte expression of antioxidants by 4-hydroxynonenal, a lipid peroxidation end product
Abstract
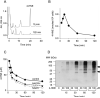
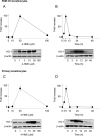
4-Hydroxynonenal (4-HNE) is a lipid peroxidation end product generated in response to oxidative stress in the skin. Keratinocytes contain an array of antioxidant enzymes which protect against oxidative stress. In these studies, we characterized 4-HNE-induced changes in antioxidant expression in mouse keratinocytes. Treatment of primary mouse keratinocytes and PAM 212 keratinocytes with 4-HNE increased mRNA expression for heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1), catalase, NADPH:quinone oxidoreductase (NQO1) and glutathione S-transferase (GST) A1-2, GSTA3 and GSTA4. In both cell types, HO-1 was the most sensitive, increasing 86-98 fold within 6h. Further characterization of the effects of 4-HNE on HO-1 demonstrated concentration- and time-dependent increases in mRNA and protein expression which were maximum after 6h with 30 μM. 4-HNE stimulated keratinocyte Erk1/2, JNK and p38 MAP kinases, as well as PI3 kinase. Inhibition of these enzymes suppressed 4-HNE-induced HO-1 mRNA and protein expression. 4-HNE also activated Nrf2 by inducing its translocation to the nucleus. 4-HNE was markedly less effective in inducing HO-1 mRNA and protein in keratinocytes from Nrf2-/- mice, when compared to wild type mice, indicating that Nrf2 also regulates 4-HNE-induced signaling. Western blot analysis of caveolar membrane fractions isolated by sucrose density centrifugation demonstrated that 4-HNE-induced HO-1 is localized in keratinocyte caveolae. Treatment of the cells with methyl-β-cyclodextrin, which disrupts caveolar structure, suppressed 4-HNE-induced HO-1. These findings indicate that 4-HNE modulates expression of antioxidant enzymes in keratinocytes, and that this can occur by different mechanisms. Changes in expression of keratinocyte antioxidants may be important in protecting the skin from oxidative stress.
Keywords: Antioxidants; Caveolae; Heme oxygenase-1; Nrf2; Skin; Stress proteins.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Regulation of keratinocyte expression of stress proteins and antioxidants by the electrophilic nitrofatty acids 9- and 10-nitrooleic acid.Free Radic Biol Med. 2014 Feb;67:1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.10.011. Epub 2013 Oct 15. Free Radic Biol Med. 2014. PMID: 24140437 Free PMC article.
-
Miltirone protects human EA.hy926 endothelial cells from oxidized low-density lipoprotein-derived oxidative stress via a heme oxygenase-1 and MAPK/Nrf2 dependent pathway.Phytomedicine. 2016 Dec 15;23(14):1806-1813. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2016.11.003. Epub 2016 Nov 4. Phytomedicine. 2016. PMID: 27912883
-
Caffeoylserotonin protects human keratinocyte HaCaT cells against H2 O2 -induced oxidative stress and apoptosis through upregulation of HO-1 expression via activation of the PI3K/Akt/Nrf2 pathway.Phytother Res. 2013 Dec;27(12):1810-8. doi: 10.1002/ptr.4931. Epub 2013 Feb 17. Phytother Res. 2013. PMID: 23418094
-
Effects of 4-hydroxynonenal on vascular endothelial and smooth muscle cell redox signaling and function in health and disease.Redox Biol. 2013 May 23;1(1):319-31. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2013.04.001. Redox Biol. 2013. PMID: 24024167 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipid peroxidation and cell cycle signaling: 4-hydroxynonenal, a key molecule in stress mediated signaling.Acta Biochim Pol. 2003;50(2):319-36. Acta Biochim Pol. 2003. PMID: 12833161 Review.
Cited by
-
Lipid peroxidation biomarkers in adolescents with or at high-risk for bipolar disorder.J Affect Disord. 2016 Mar 1;192:176-83. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2015.12.020. Epub 2015 Dec 23. J Affect Disord. 2016. PMID: 26735329 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative stress in aging human skin.Biomolecules. 2015 Apr 21;5(2):545-89. doi: 10.3390/biom5020545. Biomolecules. 2015. PMID: 25906193 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oxidative Stress and Skin Diseases: The Role of Lipid Peroxidation.Antioxidants (Basel). 2025 May 7;14(5):555. doi: 10.3390/antiox14050555. Antioxidants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40427437 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rutin as a Mediator of Lipid Metabolism and Cellular Signaling Pathways Interactions in Fibroblasts Altered by UVA and UVB Radiation.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017;2017:4721352. doi: 10.1155/2017/4721352. Epub 2017 Jan 12. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017. PMID: 28168010 Free PMC article.
-
JNK1 ablation in mice confers long-term metabolic protection from diet-induced obesity at the cost of moderate skin oxidative damage.FASEB J. 2016 Sep;30(9):3124-32. doi: 10.1096/fj.201600393R. Epub 2016 May 26. FASEB J. 2016. PMID: 27230858 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alary J, Gueraud F, Cravedi JP. Fate of 4-hydroxynonenal in vivo: disposition and metabolic pathways. Mol Aspects Med. 2003;24:177–187. - PubMed
-
- Aldini G, Granata P, Marinello C, Beretta G, Carini M, Facino RM. Effects of UVB radiation on 4-hydroxy-2-trans-nonenal metabolism and toxicity in human keratinocytes. Chem Res Toxicol. 2007;20:416–423. - PubMed
-
- Aldini G, Granata P, Orioli M, Santaniello E, Carini M. Detoxification of 4- hydroxynonenal (HNE) in keratinocytes: characterization of conjugated metabolites by liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. J Mass Spectrom. 2003;38:1160–1168. - PubMed
-
- Basu-Modak S, Luscher P, Tyrrell RM. Lipid metabolite involvement in the activation of the human heme oxygenase-1 gene. Free Radic Biol Med. 1996;20:887–897. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

