mRNA localization to P-bodies in yeast is bi-phasic with many mRNAs captured in a late Bfr1p-dependent wave
- PMID: 24424022
- PMCID: PMC3953815
- DOI: 10.1242/jcs.139055
mRNA localization to P-bodies in yeast is bi-phasic with many mRNAs captured in a late Bfr1p-dependent wave
Abstract
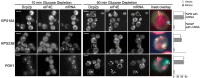
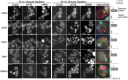
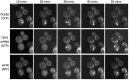
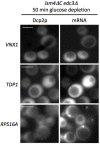
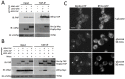
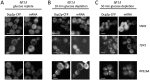
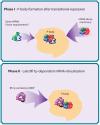
The relocalization of translationally repressed mRNAs to mRNA processing bodies Pbodies is a key consequence of cellular stress across many systems. Pbodies harbor mRNA degradation components and are implicated in mRNA decay, but the relative timing and control of mRNA relocalization to Pbodies is poorly understood. We used the MS2GFP system to follow the movement of specific endogenous mRNAs in live Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells after nutritional stress. It appears that the relocalization of mRNA to Pbodies after stress is biphasic some mRNAs are present early, whereas others are recruited much later concomitant with recruitment of translation initiation factors, such as eIF4E. We also find that Bfr1p is a latephaselocalizing Pbody protein that is important for the delayed entry of certain mRNAS to Pbodies. Therefore, for the mRNAs tested, relocalization to Pbodies varies both in terms of the kinetics and factor requirements. This work highlights a potential new regulatory juncture in gene expression that would facilitate the overall rationalization of protein content required for adaptation to stress.
Keywords: Glucose regulation; Pbodies; Stress granules; Yeast; mRNA localization.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dcp2 phosphorylation by Ste20 modulates stress granule assembly and mRNA decay in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.J Cell Biol. 2010 May 31;189(5):813-27. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200912019. J Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20513766 Free PMC article.
-
Puf1p acts in combination with other yeast Puf proteins to control mRNA stability.RNA. 2008 Feb;14(2):246-62. doi: 10.1261/rna.847408. Epub 2007 Dec 19. RNA. 2008. PMID: 18094119 Free PMC article.
-
Context-dependent deposition and regulation of mRNAs in P-bodies.Elife. 2018 Jan 3;7:e29815. doi: 10.7554/eLife.29815. Elife. 2018. PMID: 29297464 Free PMC article.
-
Yeast mRNA localization: protein asymmetry, organelle localization and response to stress.Biochem Soc Trans. 2014 Aug;42(4):1256-60. doi: 10.1042/BST20140086. Biochem Soc Trans. 2014. PMID: 25110034 Review.
-
Inhibition of translation initiation following glucose depletion in yeast facilitates a rationalization of mRNA content.Biochem Soc Trans. 2010 Aug;38(4):1131-6. doi: 10.1042/BST0381131. Biochem Soc Trans. 2010. PMID: 20659017 Review.
Cited by
-
In the right place at the right time: visualizing and understanding mRNA localization.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2015 Feb;16(2):95-109. doi: 10.1038/nrm3918. Epub 2014 Dec 30. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 25549890 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Translational Regulation of Pmt1 and Pmt2 by Bfr1 Affects Unfolded Protein O-Mannosylation.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Dec 10;20(24):6220. doi: 10.3390/ijms20246220. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31835530 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic changes in eIF4F-mRNA interactions revealed by global analyses of environmental stress responses.Genome Biol. 2017 Oct 27;18(1):201. doi: 10.1186/s13059-017-1338-4. Genome Biol. 2017. PMID: 29078784 Free PMC article.
-
Bidirectional Genetic Control of Phenotypic Heterogeneity and Its Implication for Cancer Drug Resistance.Mol Biol Evol. 2021 May 4;38(5):1874-1887. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msaa332. Mol Biol Evol. 2021. PMID: 33355660 Free PMC article.
-
MS2 coat proteins bound to yeast mRNAs block 5' to 3' degradation and trap mRNA decay products: implications for the localization of mRNAs by MS2-MCP system.RNA. 2015 Aug;21(8):1393-5. doi: 10.1261/rna.051797.115. Epub 2015 Jun 19. RNA. 2015. PMID: 26092944 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

