A novel tissue model for angiogenesis: evaluation of inhibitors or promoters in tissue level
- PMID: 24424154
- PMCID: PMC3892440
- DOI: 10.1038/srep03693
A novel tissue model for angiogenesis: evaluation of inhibitors or promoters in tissue level
Abstract
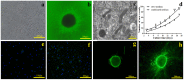
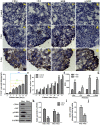
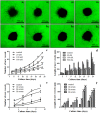
A novel tissue model for angiogenesis (TMA) is established for effective evaluation of angiogenesis inhibitors or promoters in vitro. Lung tissues were cultured in fibrinogen "sandwich" structure which resembled the formation of neovessels in vivo. The cells and capillary-like structures grew from the lung tissues were identified as endothelial cells and neovessels. Both immunohistochemisty and western blot results indicated that autocrine VEGF bound to the KDR and induced KDR autophosphorylation that could induce the proliferation of endothelial cells and their migration as well as the formation of microvessels on the lung tissue edge. With addition of the TMA, the murine VEGF and cultured medium produced by A549 tumor cells apparently promoted the increase of neovessels. Sorafenib as a tumor angiogenesis inhibitor and Tongxinluo as an angiogenesis promoter were both used to evaluate the TMA performance and they exhibited a good effect on neovessels in the TMA. The model established imitated angiogenesis in vivo and could well serve as an effective method in evaluating the angiogenesis inhibitors or promoters, and could also be practical for screening small molecules that affect blood vessel formation.
Figures

Similar articles
-
SKLB610: a novel potential inhibitor of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor tyrosine kinases inhibits angiogenesis and tumor growth in vivo.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2011;27(5):565-74. doi: 10.1159/000329978. Epub 2011 Jun 15. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2011. PMID: 21691074
-
Cultivated Orostachys japonicus extract inhibits VEGF-induced angiogenesis via regulation of VEGFR2 signaling pathway in vitro and in vivo.J Ethnopharmacol. 2020 Jun 28;256:112664. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.112664. Epub 2020 Feb 8. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32045685
-
Ginkgo biloba exocarp extracts inhibits angiogenesis and its effects on Wnt/β-catenin-VEGF signaling pathway in Lewis lung cancer.J Ethnopharmacol. 2016 Nov 4;192:406-412. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.09.018. Epub 2016 Sep 17. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27649680
-
Antiangiogenic mechanisms of PJ-8, a novel inhibitor of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor signaling.Carcinogenesis. 2012 May;33(5):1022-30. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgs127. Epub 2012 Mar 20. Carcinogenesis. 2012. PMID: 22436611
-
The Role and Research Progress of Inhibitor of Differentiation 1 in Atherosclerosis.DNA Cell Biol. 2022 Feb;41(2):71-79. doi: 10.1089/dna.2021.0745. Epub 2022 Jan 19. DNA Cell Biol. 2022. PMID: 35049366 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Advances in on-chip vascularization.Regen Med. 2017 Apr;12(3):285-302. doi: 10.2217/rme-2016-0152. Epub 2017 Mar 20. Regen Med. 2017. PMID: 28318376 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biological activity of a vascular endothelial cell-hydroxyapatite orbital implant complex: An experimental study.Exp Ther Med. 2022 Mar;23(3):227. doi: 10.3892/etm.2022.11152. Epub 2022 Jan 18. Exp Ther Med. 2022. PMID: 35222704 Free PMC article.
-
Behaviour of endothelial cells in a tridimensional in vitro environment.Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:630461. doi: 10.1155/2015/630461. Epub 2015 Feb 19. Biomed Res Int. 2015. PMID: 25789323 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of multi-target receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors as novel anti-angiogenesis agents.Sci Rep. 2017 Mar 23;7:45145. doi: 10.1038/srep45145. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28332573 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Carmeliet P. Mechanisms of angiogenesis and arteriogenesis. Nat Med 6, 389–395 (2000). - PubMed
-
- Folkman J. Tumor angiogenesis: a possible control point in tumor growth. Ann Intern Med 82, 96–100 (1975). - PubMed
-
- Carney D. N. Lung cancer–time to move on from chemotherapy. New Engl J Med 346, 126–128 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Ferrara N., Gerber H. P. & LeCouter J. The biology of VEGF and its receptors. Nat Med 9, 669–676 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Ferrara N. & Kerbel R. Angiogenesis as a therapeutic target. Nature 438, 967–974 (2005). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

